Volume 10, Number 7—July 2004
Dispatch
Mice Susceptible to SARS Coronavirus
Figure 1
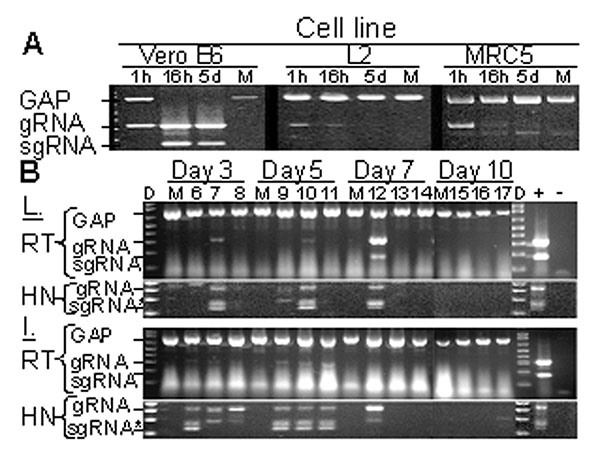
Figure 1. Replication-specific multiplex reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay shows severe acute respiratory syndrome–associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV) replicated in the lungs and intestines of mice. A. Vero E6, murine fibroblast (L2), and human lung fibroblasts (MRC5) were inoculated with SARS-CoV at an MOI of ≈ 0.001 or were mock-inoculated (M). G3PDH, SARS-CoV gRNA, and sgRNA were amplified by multiplex RT-PCR from total RNA extracted at 1 h, 16 h, or 5 days after inoculation. Amplicons were visualized by ethidium bromide staining after electrophoresis; negative images are shown. B. Mice were inoculated with 2x105 50% tissue culture infective dose of SARS-CoV (lanes labeled 6–17) or were mock-inoculated (M) and euthanized after 3, 5, 7, or 10 days. G3PDH, SARS-CoV gRNA, and sgRNA were amplified by multiplex RT-PCR from total RNA extracted from the lung (L) and intestine (I) harvested at various time points. Heminested PCR (HN) was used to amplify gRNA and sgRNA from RT-PCR reactions. Positive and negative controls for PCR reactions are indicated by + and –, respectively. D indicates DNA marker ladder. *The doublet observed in HN-PCR reactions results from residual primers used in the primary amplification reaction.