Volume 14, Number 12—December 2008
Dispatch
Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Group 1 Coronaviruses in South American Bats
Figure 2
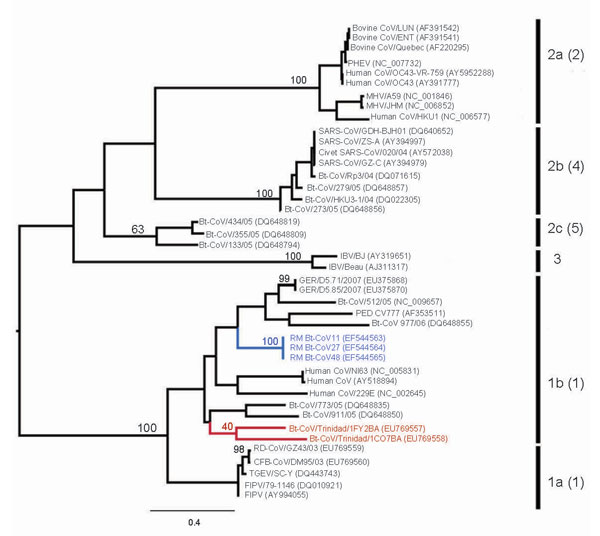
Figure 2. Maximum likelihood tree of coronaviruses based on 378-bp fragment of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene. The tree was inferred under the General Time Reversible (GTR + Γ4 + I) by using PAUP* version 4.0b (Sinauer Associates, Inc., Sunderland, MA, USA). Trinidadian bat coronavirus (Bt-CoV) sequences are highlighted in red and North American Bt-CoV in blue. Previously defined phylogenetic groups and a putative novel group (10) are delineated by the bars on the right. The numbering of these groups is as described in the eighth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses with the alternative grouping proposed by Tang et al. (4) in brackets. Bootstrap support values for groups 1a, 1b, 2a–c, 3, and the lineage containing Trinidadian Bt-CoVs are shown. GenBank accession numbers are noted in parentheses. Scale bar indicates number of nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T. Bats: important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006;19:531–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lau SK, Woo PC, Li KS, Huang Y, Tsoi HW, Wong BH, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in Chinese horseshoe bats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:14040–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Poon LL, Chu DK, Chan KH, Wong OK, Ellis TM, Leung YH, Identification of a novel coronavirus in bats. J Virol. 2005;79:2001–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tang XC, Zhang JX, Zhang SY, Wang P, Fan XH, Li LF, Prevalence and genetic diversity of coronaviruses in bats from China. J Virol. 2006;80:7481–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Woo PC, Lau SK, Li KS, Poon RW, Wong BH, Tsoi HW, Molecular diversity of coronaviruses in bats. Virology. 2006;351:180–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dominguez SR, O’Shea TJ, Oko LM, Holmes KV. Detection of group 1 coronaviruses in bats in North America. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1295–300.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gloza-Rausch F, Ipsen A, Seebens A, Göttsche M, Panning M, Felix Drexler J, Detection and prevalence patterns of group I coronaviruses in bats, northern Germany. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:626–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Muller MA, Paweska JT, Leman PA, Drosten C, Grywna K, Kemp A, Coronavirus antibodies in African bat species. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1367–70.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guan Y, Zheng BJ, He YQ, Liu XL, Zhuang ZX, Chueng CL, Isolation and characterization of viruses related to the SARS coronavirus from animals in southern China. Science. 2003;302:276–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Posada D, Crandall KA. Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics. 1998;14:817–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dong BQ, Liu W, Fan XH, Vijaykrishna D, Tang XC, Gao F, Detection of a novel and highly divergent coronavirus from Asian leopard cats and Chinese ferret badgers in Southern China. J Virol. 2007;81:6920–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gorbalenya AE, Snijder EJ, Spaan WJ. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus phylogeny: toward consensus. J Virol. 2004;78:7863–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hamre D, Procknow JJ. A new virus isolated from the human respiratory tract. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966;121:190–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- van der Hoek L, Pyrc K, Jebbink MF, Vermeulen-Oost W, Berkhout RJ, Wolthers KC, Identification of a new human coronavirus. Nat Med. 2004;10:368–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fouchier RA, Hartwig NG, Bestebroer TM, Niemeyer B, de Jong JC, Simon JH, A previously undescribed coronavirus associated with respiratory disease in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:6212–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar