Volume 15, Number 2—February 2009
Research
Seoul Virus and Hantavirus Disease, Shenyang, People’s Republic of China
Figure 1
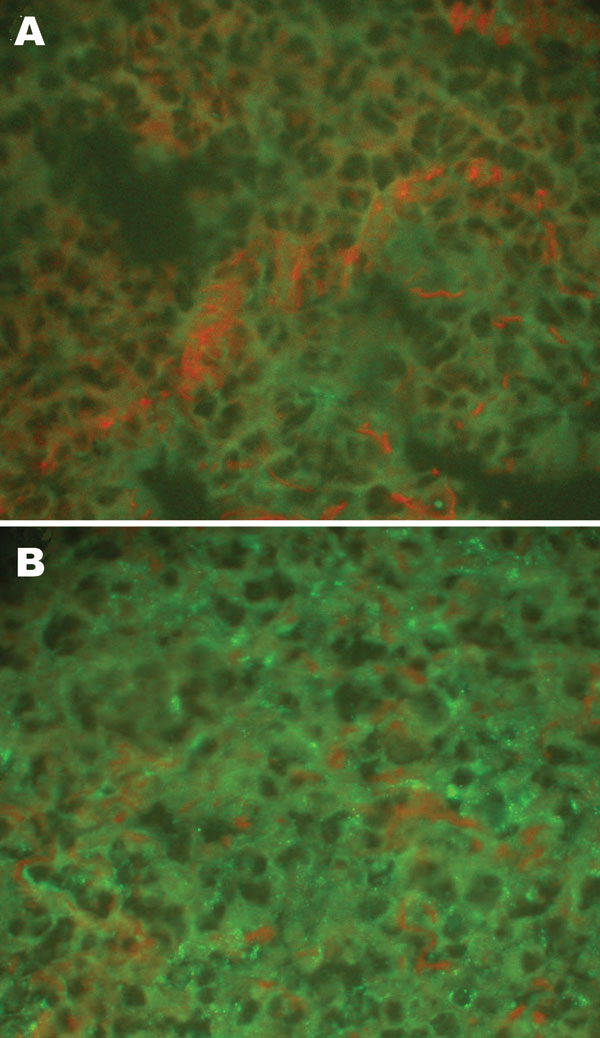
Figure 1. Detection of hantaviral antigens by indirect immunofluorescent assay. A) Hantaviral antigen- negative Rattus norvegicus lung tissue, detected with anti-L99 and 76-118 hantavirus sera. B) Hantaviral antigen-positive R. norvegicus lung tissue, detected with anti-L99 and 76-118 hantavirus antibodies. Magnification ×400.
Page created: December 08, 2010
Page updated: December 08, 2010
Page reviewed: December 08, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.