Volume 9, Number 10—October 2003
Research
Cephamycin Resistance in Clinical Isolates and Laboratory-derived Strains of Escherichia coli, Nova Scotia, Canada
Figure 1
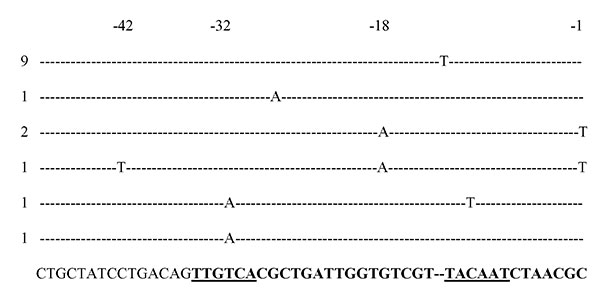
Figure 1. Sequences of Escherichia coli AmpC promoters showing mutations detected in cephamycin-resistant strains. The consensus sequence for E. coli K12 is shown in the last row. The promoter region is in boldface. The –35 and –10 (Pribnow box) hexamers are underlined. The number of strains with these mutations is indicated on the left.
Page created: January 10, 2011
Page updated: January 10, 2011
Page reviewed: January 10, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.