Volume 15, Number 2—February 2009
Research
Characteristics of 263K Scrapie Agent in Multiple Hamster Species
Figure 1
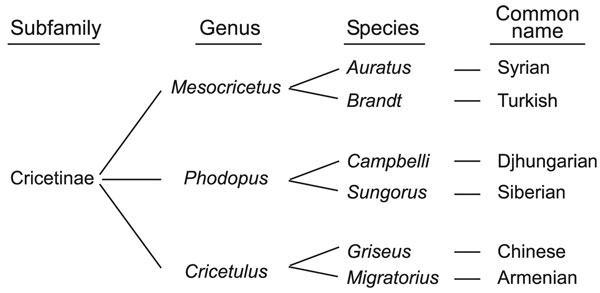
Figure 1. Taxonomic classification for 6 hamster species. Phylogenetically, these species are grouped into closely related taxonomic genera (9).
References
- Race R, Meade-White K, Raines A, Raymond GJ, Caughey B, Chesebro BJ. Subclinical scrapie infection in a resistant species: persistence, replication, and adaptation of infectivity during four passages. J Infect Dis. 2002;186(Suppl 2):S166–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Goldmann W, Hunter N, Benson G, Foster JD, Hope JJ. Different scrapie-associated fibril proteins (PrP) are encoded by lines of sheep selected for different alleles of the Sip gene. J Gen Virol. 1991;72:2411–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Westaway D, Zuliani V, Cooper CM, Da CM, Neuman S, Jenny AL, Homozygosity for prion protein alleles encoding glutamine-171 renders sheep susceptible to natural scrapie. Genes Dev. 1994;8:959–69. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bossers A, Schreuder BE, Muileman IH, Belt PB, Smits MA. PrP genotype contributes to determining survival times of sheep with natural scrapie. J Gen Virol. 1996;77:2669–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jewell JE, Conner MM, Wolfe LL, Miller MW, Williams ES. Low frequency of PrP genotype 225SF among free-ranging mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) with chronic wasting disease. J Gen Virol. 2005;86:2127–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Meade-White K, Race B, Trifilo M, Bossers A, Favara C, Lacasse R, Resistance to chronic wasting disease in transgenic mice expressing a naturally occurring allelic variant of deer prion protein. J Virol. 2007;81:4533–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Westaway D, Goodman PA, Mirenda CA, McKinley MP, Carlson GA, Prusiner SB. Distinct prion proteins in short and long scrapie incubation period mice. Cell. 1987;51:651–62. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barron RM, Thomson V, King D, Shaw J, Melton DW, Manson JCJ. Transmission of murine scrapie to P101L transgenic mice. J Gen Virol. 2003;84:3165–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Conroy CJ, Cook J. MtDNA evidence for repeated pulses of speciation within arvicoline and murid rodents. J Mamm Evol. 1999;6:221–45. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Kimberlin RH, Walker CA. Evidence that the transmission of one source of scrapie agent to hamsters involves separation of agent strains from a mixture. J Gen Virol. 1978;39:487–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dougherty RM. Animal virus titration techniques. In: Techniques in experimental virology. New York: Academic Press, Inc.; 1964.
- Chesebro B, Trifilo M, Race R, Meade-White K, Teng C, LaCasse R, Anchorless prion protein results in infectious amyloid disease without clinical scrapie. Science. 2005;308:1435–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Oldstone MB, Race R, Thomas D, Lewicki H, Homann D, Smelt S, Lymphotoxin-alpha- and lymphotoxin-beta-deficient mice differ in susceptibility to scrapie: evidence against dendritic cell involvement in neuroinvasion. J Virol. 2002;76:4357–63. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Race R, Jenny A, Sutton DJ. Scrapie infectivity and proteinase K-resistant prion protein in sheep placenta, brain, spleen, and lymph node: implications for transmission and antemortem diagnosis. J Infect Dis. 1998;178:949–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Caughey B, Raymond GJ, Ernst D, Race RE. N-terminal truncation of the scrapie-associated form of PrP by lysosomal protease(s): implications regarding the site of conversion of PrP to the protease-resistant state. J Virol. 1991;65:6597–603.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Race BL, Meade-White KD, Ward A, Jewell J, Miller MW, Williams ES, Levels of abnormal prion protein in deer and elk with chronic wasting disease. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:824–30.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Scott M, Groth D, Foster D, Torchia M, Yang SL, DeArmond SJ, Propagation of prions with artificial properties in transgenic mice expressing chimeric PrP genes. Cell. 1993;73:979–88. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Collinge J, Sidle KC, Meads J, Ironside J, Hill AF. Molecular analysis of prion strain variation and the aetiology of “new variant” CJD. Nature. 1996;383:685–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hill AF, Desbruslais M, Joiner S, Sidle KC, Gowland I, Collinge J, The same prion strain causes vCJD and BSE. Nature. 1997;389:448–50, 526.
- Parchi P, Capellari S, Chen SG, Petersen RB, Gambetti P, Kopp N, Typing prion isoforms. Nature. 1997;386:232–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bessen RA, Marsh RF. Biochemical and physical properties of the prion protein from two strains of the transmissible mink encephalopathy agent. J Virol. 1992;66:2096–101.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bessen RA, Marsh RF. Distinct PrP properties suggest the molecular basis of strain variation in transmissible mink encephalopathy. J Virol. 1994;68:7859–68.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bessen RA, Kocisko DA, Raymond GJ, Nandan S, Lansbury PT, Caughey B. Non-genetic propagation of strain-specific properties of scrapie prion protein. Nature. 1995;375:698–700. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fraser H, Dickinson AG. The sequential development of the brain lesions of scrapie in three strains of mice. J Comp Pathol. 1968;78:301–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kimberlin RH, Cole S, Walker CAJ. Temporary and permanent modifications to a single strain of mouse scrapie on transmission to rats and hamsters. J Gen Virol. 1987;68:1875–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kimberlin RH, Walker CA, Fraser HJ. The genomic identity of different strains of mouse scrapie is expressed in hamsters and preserved on reisolation in mice. J Gen Virol. 1989;70:2017–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Basler K, Oesch B, Scott M, Westaway D, Walchli M, Groth DF, Scrapie and cellular PrP isoforms are encoded by the same chromosomal gene. Cell. 1986;46:417–28. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lowenstein DH, Butler DA, Westaway D, McKinley MP, DeArmond SJ, Prusiner SB. Three hamster species with different scrapie incubation times and neuropathological features encode distinct prion proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:1153–63.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Oesch B, Westaway D, Walchli M, McKinley MP, Kent SB, Aebersold R, A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985;40:735–46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schatzl HM, Da CM, Taylor L, Cohen FE, Prusiner SBJ. Prion protein gene variation among primates. J Mol Biol. 1995;245:362–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Collinge J, Harding AE, Owen F, Poulter M, Lofthouse R, Boughey AM, Diagnosis of Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome in familial dementia with prion protein gene analysis. Lancet. 1989;2:15–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Goldfarb LG, Brown P, McCombie WR, Goldgaber D, Swergold GD, Wills PR, Transmissible familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease associated with five, seven, and eight extra octapeptide coding repeats in the PRNP gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88:10926–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barron RM, Manson JC. A gene-targeted mouse model of P102L Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome. Clin Lab Med. 2003;23:161–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Supattapone S, Muramoto T, Legname G, Mehlhorn I, Cohen FE, DeArmond SJ, Identification of two prion protein regions that modify scrapie incubation time. J Virol. 2001;75:1408–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- James TL, Liu H, Ulyanov NB, Farr-Jones S, Zhang H, Donne DG, Solution structure of a 142-residue recombinant prion protein corresponding to the infectious fragment of the scrapie isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:10086–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Liu H, Farr-Jones S, Ulyanov NB, Llinas M, Marqusee S, Groth D, Solution structure of Syrian hamster prion protein rPrP(90-231). Biochemistry. 1999;38:5362–77. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: December 08, 2010
Page updated: December 08, 2010
Page reviewed: December 08, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.