Volume 16, Number 10—October 2010
Dispatch
Hepatitis E Virus Genotype Diversity in Eastern China
Figure 1
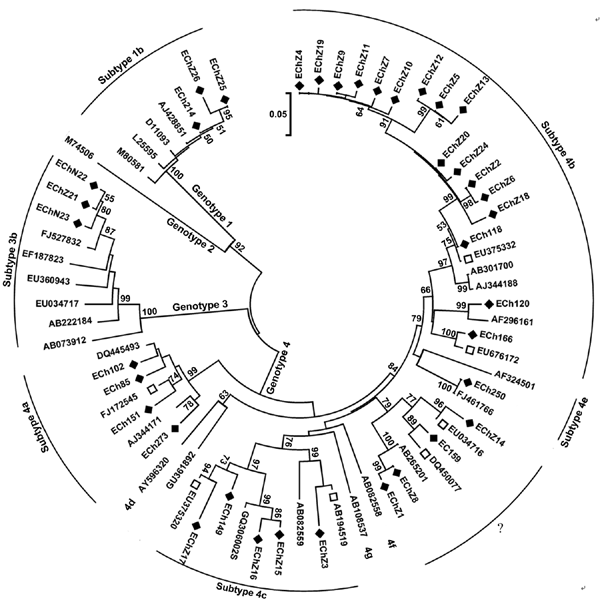
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of hepatitis E virus isolates in eastern China, 2007–2009. The phylogenetic tree was produced with a 348-nt open reading frame 2 sequence alignment of 37 isolates from this study and other 31 reference sequences, using the neighbor-joining method and evaluated by using the interior branch test method with MEGA4 software (www.megasoftware.net). Percentage of bootstrap support is shown by values at the branch nodes of the tree. Only nodes with a bootstrap value >50 are labeled; these values are the result of resampling the data 1,000 times. Black diamonds, isolates identified in the current study; white squares, GenBank sequences with the highest sequence homology to our sequences; ?, genotype 4 strains that could not be subtyped but closely clustered with each other, forming a new subtype. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per position.