Volume 17, Number 12—December 2011
Research
Isolation of Prion with BSE Properties from Farmed Goat
Figure 3
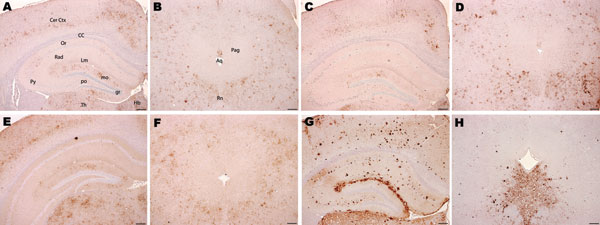
Figure 3. Immunohistochemical analysis of brains of host-encoded prion protein (PrP)-b mice (VM) inoculated with (A and B) fixed material from the goat with suspected case, (C and D) fixed material from experimental goat bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), (E and F) unfixed material from experimental sheep BSE, and (G and H) fixed material from experimental goat scrapie. In thalamus, cerebral cortex, and hippocampus the suspected case (A) and the BSE controls (C and E) showed mainly granular PrPSc deposits with comparable distribution. In the scrapie control (G), the predominant PrPSc type was large aggregates and plaques. In the periaqueductal gray matter, mice challenged with the suspected case (B) and with BSE controls (D and F) showed a manifold lower staining intensity of PrPSc labeling compared with the surrounding area, but the scrapie control (H) showed an intense labeling in the ventral periaqueductal region associated with substantial reduction of labeling in all neighboring areas. Aq, aqueduct; CC, corpus callosum; Cer Ctx, cerebral cortex; Hb, habenular nuclei; Rn, raphe nucleus; Pag, periaqueductal gray; Th, thalamus; Or, Py, Rad, and Lm, oriens, pyramidal cell, radiatum, and lacunosum-moleculare layers, respectively, of the hippocampus; gr, mo, and po, granular, molecular, and polymorph layers, respectively, of the dentate gyrus. Scale bars = 200 μm.