Volume 17, Number 2—February 2011
Letter
Rickettsia aeschlimannii in Hyalomma marginatum Ticks, Germany
Figure
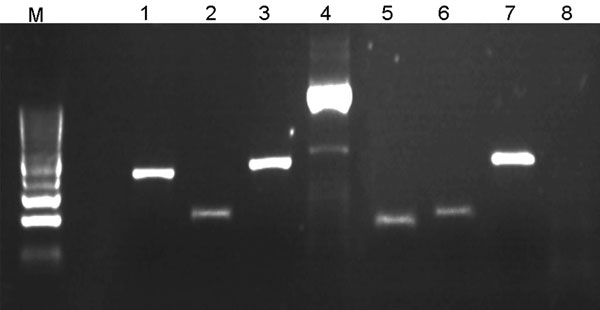
Figure. Illustration of multispacer typing. Amplicons 1–4 result from PCRs on DNA obtained from 1 Rickettsia raoultii–infected Dermacentor reticulatus tick isolate; lanes 5–8 result from PCRs on 1 damaged isolate. PCRs amplifying dksA-xerC (lanes 1 and 5), mppA-purC (lanes 2 and 6), and rpmE-tRNA (lanes 3 and 7) intergenic spacers were performed as described (5). PCR amplifying the entire internal transcribed factor 2 (ITS2) locus of D. reticulatus tick (lanes 4 and 8) was involved in each PCR run as a positive control and for validation of D. reticulatus tick identity (the primers will be described elsewhere).The negative result of ITS2 PCR with the damaged isolates (lane 8) indicated that they are not D. reticulatus ticks. Lane M, DNA size marker (100-bp ladder). PCR products were directly sequenced in both directions with respective primers by an ABI PRISM DNA Sequencer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). DNA Star package (DNA Star, Madison, WI, USA) and the tools offered by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) were used for DNA search and analysis.
References
- Parola P, Paddock C, Raoult D. Tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: emerging diseases challenging old concepts. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005;18:719–56. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dobler G, Wölfel R. Typhus and other rickettsioses. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2009;106:348–54.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Parola P, Rovery C, Rolain JM, Brouqui P, Davoust B, Raoult D. Rickettsia slovaca and R. raoultii in tick-borne rickettsioses. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:1105–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pluta S, Tewald F, Hartelt K, Oehme R, Kimmig P, Mackenstedt U. Rickettsia slovaca in Dermacentor marginatus ticks, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15:2077–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fournier PE, Raoult D. Identification of rickettsial isolates at the species level using multi-spacer typing. BMC Microbiol. 2007;7:72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Caporale DA, Rich SM, Spielman A, Telford SR III, Kocher TD. Discriminating between Ixodes ticks by means of mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 1995;4:361–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rees DJ, Dioli M, Kirkendall LR. Molecules and morphology: evidence for cryptic hybridization in African Hyalomma (Acari: Ixodidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2003;27:131–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shpynov S, Rudakov N, Tohkov Y, Matushchenko A, Tarasevich I, Raoult D, Detection of Rickettsia aeschlimannii in Hyalomma marginatum ticks in western Russia. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009;15(Suppl 2):S315–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kampen H, Poltz W, Hartelt K, Wölfel R, Faulde M. Detection of a questing Hyalomma marginatum marginatum adult female (Acari, Ixodidae) in southern Germany. Exp Appl Acarol. 2007;43:227–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Raoult D, Roux V. Rickettsioses as paradigms of new or emerging infectious diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1997;10:694–719.PubMedGoogle Scholar