Volume 19, Number 1—January 2013
Research
Novel Polyomavirus associated with Brain Tumors in Free-Ranging Raccoons, Western United States
Figure 2
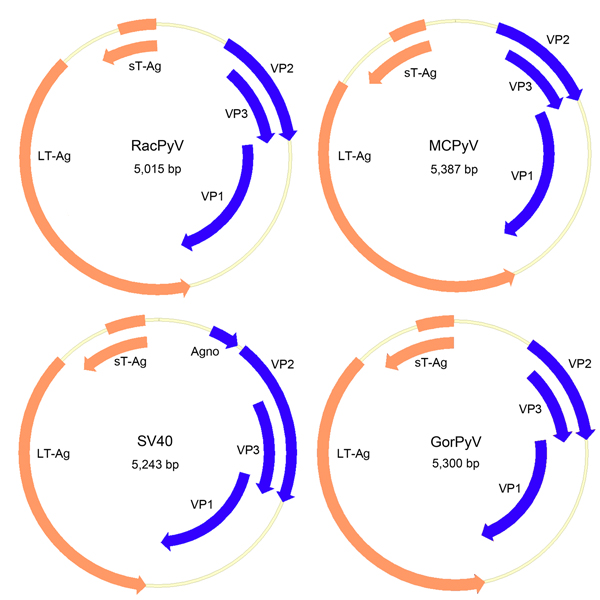
Figure 2. . Genome organization of RacPyV. The entire dsDNA viral genome for RacPyV10 comprises 5,015 bp. The viral genome has a noncoding regulatory region and putative open reading frames for the late proteins VP1, VP2, and VP3 and the early proteins LT-Ag and sT-Ag. MCPyV and GorPyV, which are phylogenetic neighbors, and SV40 are presented for comparison. RacPyV, raccoon polyomavirus; LT-Ag, large T-antigen; sT-Ag, small T-antigen; VP, viral protein; MCPyV, Merkel cell polyomavirus; SV40, simian virus 40. GorPyV, gorilla polyomavirus.
Page created: December 21, 2012
Page updated: December 21, 2012
Page reviewed: December 21, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.