Clinical, Environmental, and Serologic Surveillance Studies of Melioidosis in Gabon, 2012–2013
W. Joost Wiersinga
1
, Emma Birnie
1, Tassili A.F. Weehuizen, Abraham S. Alabi, Michaëla A.M. Huson, Robert A. G. Huis in ’t Veld, Harry K. Mabala, Gregoire K. Adzoda, Yannick Raczynski-Henk, Meral Esen, Bertrand Lell, Peter G. Kremsner, Caroline E. Visser, Vanaporn Wuthiekanun, Sharon J. Peacock, Arie van der Ende, Direk Limmathurotsakul, and Martin P. Grobusch
Author affiliations: University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands (W.J. Wiersinga, E. Birnie, T.A.F. Weehuizen, M.A.M. Huson, R.A.G. in ’t Veld, C.E. Visser, A. van der Ende, M.P. Grobusch); Albert Schweitzer Hospital, Lambaréné, Gabon (A.S. Alabi, H.K. Mabala, G.K. Adzoda, M. Esen, B. Lell, P.G. Kremsner, M.P. Grobusch); Ex-Situ Silex Geoarchaeology, Leiden, the Netherlands (Y. Raczynski-Henk); University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany (M. Esen, B. Lell, P.G. Kremsner, M.P. Grobusch); Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand (V. Wuthiekanun, D. Limmathurotsakul); University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK (S.J. Peacock)
Main Article
Figure 2
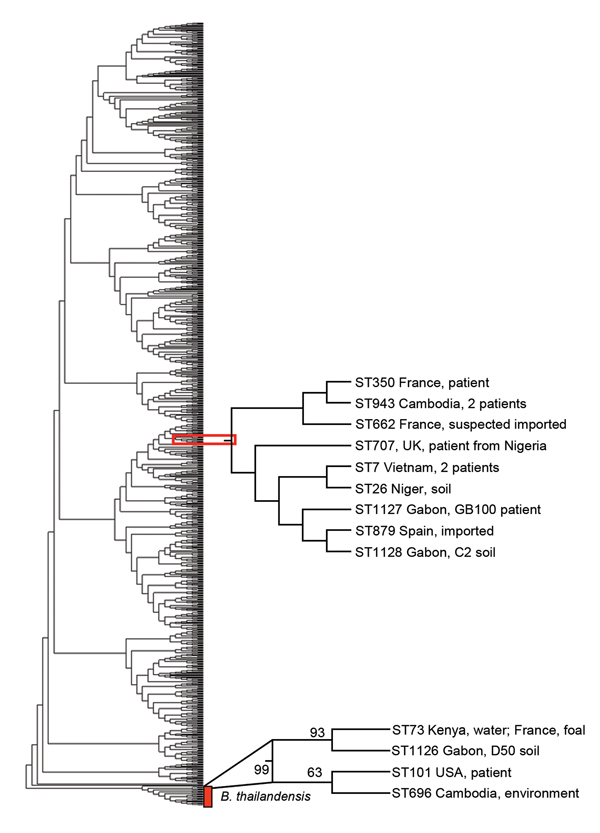
Figure 2. Phylogenetic tree of Burkholderia pseudomallei and B. thailandensis strains from Gabon, 2012–2013. Phylogenetic analysis by multilocus sequence typing amplification (MLST) of isolate Gb100 (from 62-year-old patient who died of melioidosis), B. pseudomallei soil isolate C2 (sample collected at site C), and B. thailandensis soil isolate D50 (sample collected at site D), together with sequence types representing all B. pseudomallei and B. thailandensis isolate accessible in the MLST database. Phylogenetic tree was constructed by using the neighbor-joining algorithm with the Kimura 2-parameter model. Bootstrap test was for 500 repetitions. Sequence type labels were omitted for simplicity. Position of the isolates from Gabon, including their closest relatives, are indicated.
Main Article
Page created: December 17, 2014
Page updated: December 17, 2014
Page reviewed: December 17, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
