Volume 21, Number 1—January 2015
Dispatch
Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus Serotype SAT 3 in Long-Horned Ankole Calf, Uganda
Figure 1
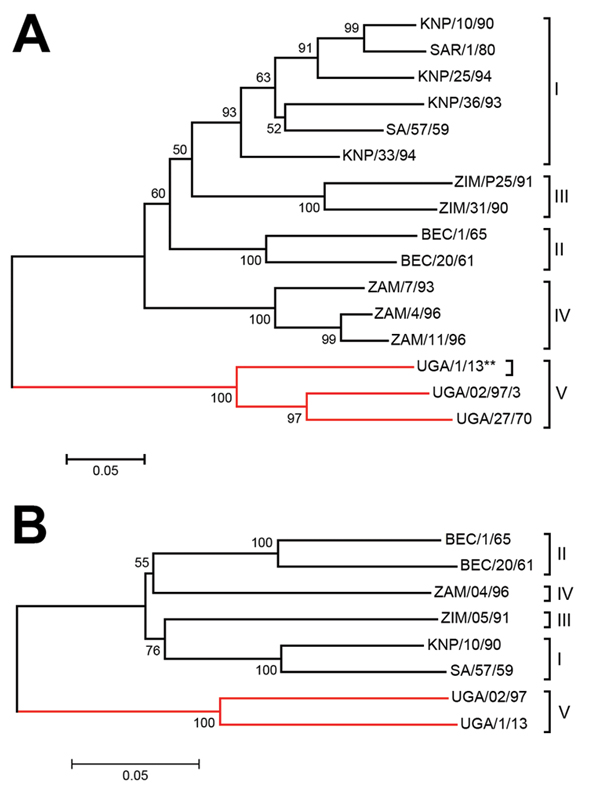
Figure 1. Neighbor-joining trees showing the relationships between A) the partial VP1 coding sequences (390 nt) and B) the complete P1 capsid protein coding sequence (2223 nt) from the SAT 3 FMDV UGA/1/13 isolate (marked with **) and other SAT 3 FMDVs within the indicated topotypes defined previously (5; http://www.wrlfmd.org/fmdv_seqs/fmdv-sat3_seq.aspx). The branches containing the Uganda viruses are indicated by the red lines. Sequences, other than for UGA/1/13, were obtained from GenBank and have been published previously (5,11–13). Bootstrap values are indicated. BEC, Bechuanaland (former name for Botswana); FMDV, foot-and-mouth disease virus; KNP, Kruger National Park (in South Africa); P1, precursor for the 4 capsid proteins; SAT, Southern African Territories; SAR, Republic of South Africa; UGA, Uganda; VP, viral protein; ZAM, Zambia; ZIM, Zimbabwe; I–V, topotypes. Scale bars indicate nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Knight-Jones TJ, Rushton J. The economic impacts of foot and mouth disease—what are they, how big are they and where do they occur? Prev Vet Med. 2013;112:161–73. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jamal SM, Belsham GJ. Foot and mouth disease; past, present and future. Vet Res. 2013;44:116. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sangula AK, Siegismund HR, Belsham GJ, Balinda SN, Masembe C, Muwanika VB. Low diversity of foot-and-mouth disease serotype C virus in Kenya: evidence for probable vaccine strain re-introductions in the field. Epidemiol Infect. 2011;139:189–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ahmed HA, Salem SA, Habashi AR, Arafa AA, Aggour MG, Salem GH, Emergence of foot-and-mouth disease virus SAT 2 in Egypt during 2012. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2012;59:476–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bastos AD, Anderson EC, Bengis RG, Keet DF, Winterbach HK, Thomson GR. Molecular epidemiology of SAT3-type foot-and-mouth disease. Virus Genes. 2003;27:283–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ayebazibwe C, Mwiine FN, Tjornehoj K, Balinda SN, Muwanika VB, Ademun Okurut AR, The role of African buffalos (Syncerus caffer) in the maintenance of foot-and-mouth disease in Uganda. BMC Vet Res. 2010;6:54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Callahan JD, Brown F, Osorio FA, Sur JH, Kramer E, Long GW, Use of a portable real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay for rapid detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2002;220:1636–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stenfeldt C, Lohse L, Belsham GJ. The comparative utility of oral swabs and probang samples for detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus infection in cattle and pigs. Vet Microbiol. 2013;162:330–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alexandersen S, Zhang Z, Donaldson AI, Garland AJ. The pathogenesis and diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease. J Comp Pathol. 2003;129:1–36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol. 2011;28:2731–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bastos AD. Detection and characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus in sub-Saharan Africa. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1998;65:37–47 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Samuel AR, Knowles NJ. Foot-and-mouth disease type O viruses exhibit genetically and geographically distinct evolutionary lineages (topotypes). J Gen Virol. 2001;82:609–21 .PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Carrillo C, Tulman ER, Delhon G, Lu Z, Carreno A, Vagnozzi A, Comparative genomics of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 2005;79:6487–504. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar