Volume 23, Number 2—February 2017
Research
Swine Influenza Virus (H1N2) Characterization and Transmission in Ferrets, Chile
Figure 4
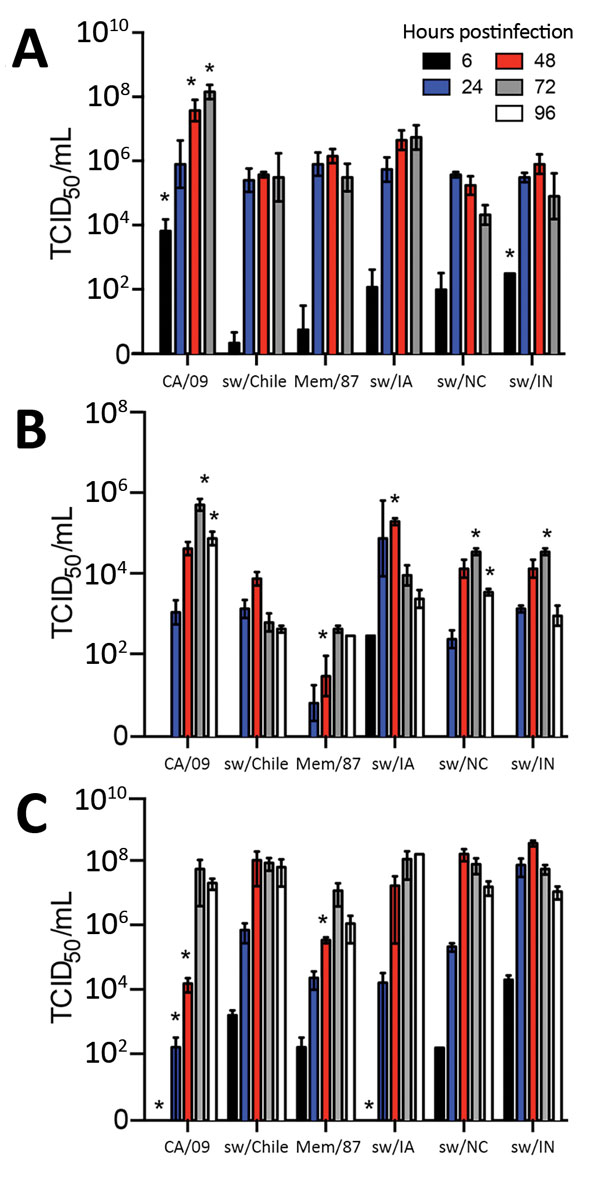
Figure 4. Replication of influenza viruses in vitro. MDCK cells (A), primary normal human bronchial epithelial cells (B), or primary swine nasal epithelial cells (C) were grown in an air-liquid interface and infected with the indicated viruses at a multiplicity of infection of 0.01. Cell culture supernatants were collected at 6 hours postinfection (hpi), 24 hpi, 48 hpi, and 72 hpi, for MDCK cells and 6 hpi, 24 hpi, 48 hpi, 72 hpi, and 96 hpi for primary normal human bronchial epithelial cells and primary swine nasal epithelial cells, and viral titers were determined by 50% tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50) analysis. Data are presented as mean titer of 3 replicates ± SEM. *p<0.05 versus sw/Chile virus.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.