Volume 25, Number 11—November 2019
Research Letter
Mutation and Diversity of Diphtheria Toxin in Corynebacterium ulcerans
Figure
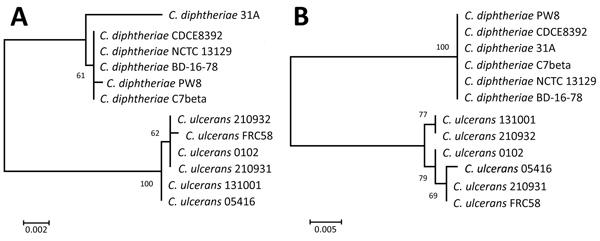
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequences (A) and amino acid sequences (B) of diphtheria toxin genes of 6 Coynebacterium ulcerans strains and 6 C. ulcerans strains. All strains had the diphtheria toxin gene; whole-genome analysis data are available from the National Center for Biotechnology Information database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome). We generated phylogenetic trees by using the maximum-likelihood method in MEGA 7.0 (https://www.megasoftware.net). 16S rRNA gene sequences were analyzed by the Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano model with 1,000 bootstrap replications; amino acid sequences were analyzed by the Whelan and Goldman model with 100 bootstrap replications. Scale bars indicate substitutions per site.
Page created: October 15, 2019
Page updated: October 15, 2019
Page reviewed: October 15, 2019
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.