Volume 25, Number 6—June 2019
Research
Enhancement of Risk for Lyme Disease by Landscape Connectivity, New York, New York, USA
Figure 3
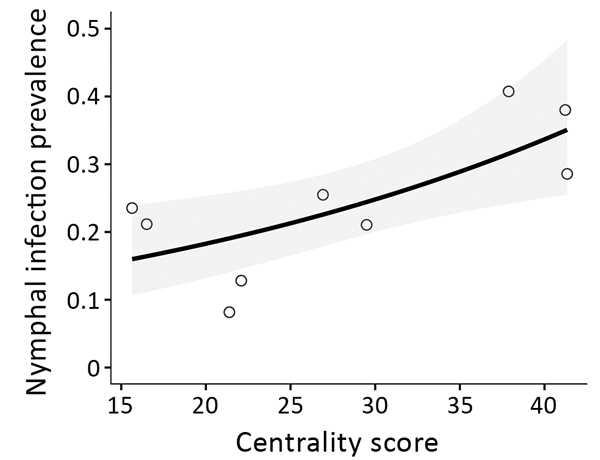
Figure 3. Ixodes scapularis tick nymphal infection prevalence and flow centrality model for Staten Island, New York, USA, 2017. The centrality score of 9 parks was the best predictor for nymphal infection prevalence. Shown are results of the binomial generalized linear model (p = 0.009). SE (± 0.1040) is indicated in gray. The coefficient estimate is 0.2714.
Page created: May 20, 2019
Page updated: May 20, 2019
Page reviewed: May 20, 2019
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.