Volume 26, Number 5—May 2020
Research Letter
Risk for Transportation of Coronavirus Disease from Wuhan to Other Cities in China
Figure
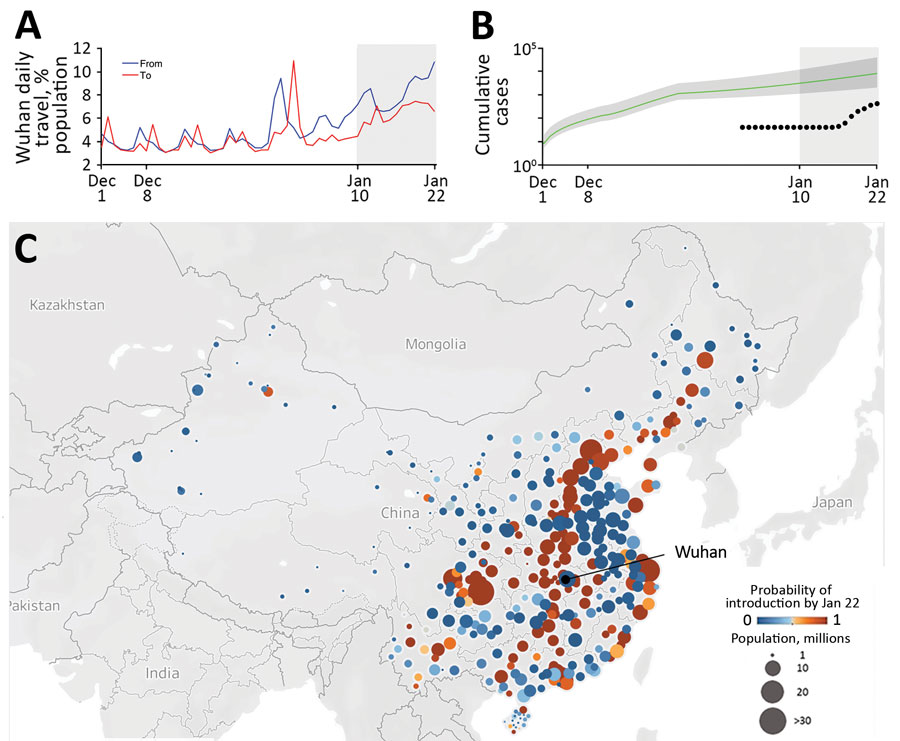
Figure. Risks for transportation of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) from Wuhan, China, before a quarantine was imposed on January 23, 2020. A) Daily travel volume to and from Wuhan, given as a percentage of the Wuhan population. Gray shading indicates the start of Spring Festival season on January 10, 2020, a peak travel period in China. B) Estimated and reported daily prevalence of COVID-19 in Wuhan. The green line and shading indicate model estimates of cumulative cases since December 1, 2019, with 95% credible interval bounds, assuming an epidemic doubling time of 7.31 days (95% credible interval 6.26–9.66 days). Black dots indicate cumulative confirmed case counts during January 1–22, 2020 (10). Gray shading at right indicates the start of Spring Festival season. C) Probability that >1 COVID-19 case infected in Wuhan traveled to cities in China by January 22, 2020. The 131 cities with a risk threshold >50% are indicated in shades of orange; 239 cities below that threshold are indicated in shades of blue. Map generated by using Mapbox (https://www.mapbox.com).
References
- Wuhan Municipal Health Commission. Wuhan Municipal Health Commission briefing on the pneumonia epidemic situation 31 Dec 2019 [in Chinese]. 2020 [cited 2020 Jan 11]. http://wjw.wuhan.gov.cn/front/web/showDetail/2019123108989
- World Health Organization. Statement on the second meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee regarding the outbreak of novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Geneva: the Organization; 2020 [cited 2020 Feb 5]. https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-meeting-of-the-international-health-regulations-(2005)-emergency-committee-regarding-the-outbreak-of-novel-coronavirus-(2019-ncov)
- Imai N, Dorigatti I, Cori A, Donnelly C, Riley S, Ferguson NM. MRC Centre for Global Infectious Disease Analysis. News 2019-nCoV. Report 2: estimating the potential total number of novel coronavirus cases in Wuhan City, China. London: Imperial College London; 2020 [cited 2020 Feb 5]. https://www.imperial.ac.uk/media/imperial-college/medicine/sph/ide/gida-fellowships/2019-nCoV-outbreak-report-22-01-2020.pdf
- Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2020;
NEJMoa2001316 ; Epub ahead of print. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - World Health Organization. Disease outbreak news: novel coronavirus—Thailand (ex-China). 2020 Jan 14 [cited 2020 Jan 27]. https://www.who.int/csr/don/14-january-2020-novel-coronavirus-thailand-ex-china/en
- Wilder-Smith A, Teleman MD, Heng BH, Earnest A, Ling AE, Leo YS. Asymptomatic SARS coronavirus infection among healthcare workers, Singapore. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:1142–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chan JF-W, Yuan S, Kok K-H, To KK-W, Chu H, Yang J, et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet. 2020;
S0140-6736(20)30154-9 ; Epub ahead of print. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Wuhan Municipal Health Commission. Bulletin on pneumonitis associated with new coronavirus infection [In Chinese] [cited 2020 Jan 29]. http://wjw.wuhan.gov.cn/front/web/list2nd/no/710
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.