Volume 30, Number 10—October 2024
Research Letter
Establishment of Amblyomma maculatum Ticks and Rickettsia parkeri in the Northeastern United States
Figure 1
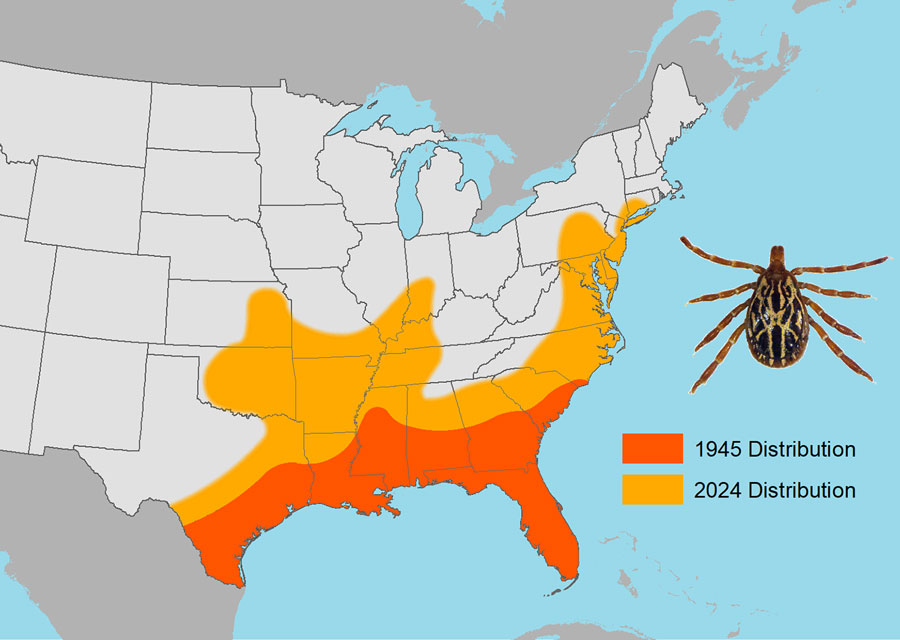
Figure 1. Generalized distributions of the Gulf Coast tick, Amblyomma maculatum (pictured), a human-biting tick species newly established in the northeastern United States, in 1945 compared with 2024. Establishment was defined as >6 ticks of the same life stage identified within a 12-month period or ticks of >1 life stage identified within a 12-month period. Data from references 2–9, https://www.dep.pa.gov/Business/ProgramIntegration/Vector-Management/Ticks/Pages/default.aspx, and https://www.in.gov/health/idepd/zoonotic-and-vectorborne-epidemiology-entomology/vector-borne-diseases/tick-borne-diseases/amblyomma-maculatum-gulf-coast-tick/#Geographic_Distribution.
References
- Molaei G, Eisen LM, Price KJ, Eisen RJ. Range expansion of native and invasive ticks: a looming public health threat. J Infect Dis. 2022;226:370–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Paddock CD, Goddard J. The evolving medical and veterinary importance of the Gulf Coast tick (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 2015;52:230–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bishopp FC, Trembley HL. Distribution and hosts of certain North American ticks. J Parasitol. 1945;31:1–54. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Phillips VC, Zieman EA, Kim CH, Stone CM, Tuten HC, Jiménez FA. Documentation of the expansion of the Gulf Coast tick (Amblyomma maculatum) and Rickettsia parkeri: first report in Illinois. J Parasitol. 2020;106:9–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maestas LP, Reeser SR, McGay PJ, Buoni MH. Surveillance for Amblyomma maculatum (Acari: Ixodidae) and Rickettsia parkeri (Rickettsiales: Rickettsiaceae) in the state of Delaware, and their public health implications. J Med Entomol. 2020;57:979–83. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Molaei G, Little EAH, Khalil N, Ayres BN, Nicholson WL, Paddock CD. Established population of the Gulf Coast tick, Amblyomma maculatum (Acari: Ixodidae), infected with Rickettsia parkeri (Rickettsiales: Rickettsiaceae), in Connecticut. J Med Entomol. 2021;58:1459–62. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bajwa WI, Tsynman L, Egizi AM, Tokarz R, Maestas LP, Fonseca DM. The Gulf Coast tick, Amblyomma maculatum (Ixodida: Ixodidae), and spotted fever group Rickettsia in the highly urbanized northeastern United States. J Med Entomol. 2022;59:1434–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ramírez-Garofalo JR, Curley SR, Field CE, Hart CE, Thangamani S. Established populations of Rickettsia parkeri-infected Amblyomma maculatum ticks in New York City, New York, USA. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022;22:184–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Musnoff BL, Cuadera MKQ, Birney MR, Zipper L, Nicholson W, Ayres B, et al. The first record of an established population of Amblyomma maculatum (Acari: Ixodidae) in New Jersey, USA. J Med Entomol. 2024;61:1081–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Eisen RJ, Paddock CD. Tick and tickborne pathogen surveillance as a public health tool in the United States. J Med Entomol. 2021;58:1490–502. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: August 08, 2024
Page updated: September 24, 2024
Page reviewed: September 24, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.