Volume 30, Number 6—June 2024
Dispatch
Zoonotic Ancylostoma ceylanicum Infection in Coyotes from Guanacaste Conservation Area, Costa Rica, 2021
Figure 2
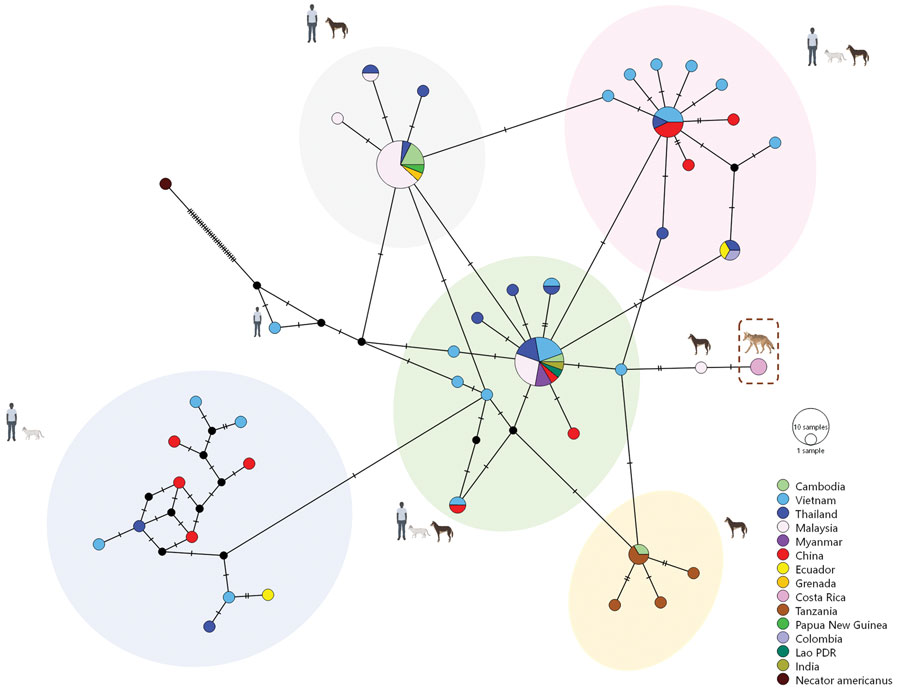
Figure 2. Median joining haplotype network showing global Ancylostoma ceylanicum sequences for cats, humans, and dogs and coyotes from Guanacaste Conservation Area, Costa Rica, 2021 (dashed box). Each circle represents a haplotype; circle size is proportional to the number of animals and persons with that haplotype, with the proportion found in each country indicated by color. A hatch mark across a line represents a mutation step between haplotypes. The legend illustrates color-coded haplotypes corresponding to each country. In addition, icons representing humans, dogs, cats, and coyotes are juxtaposed with each haplotype cluster to indicate host origins.
Page created: April 19, 2024
Page updated: May 22, 2024
Page reviewed: May 22, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.