Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Volume 31, Number 5—May 2025
Research Letter
Emergence of Feline Sporotrichosis near Brazil Border, Argentina, 2023–2024
Suggested citation for this article
Abstract
We describe a large urban outbreak of feline sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis fungi in Argentina. Over a 7-month period in Puerto Iguazú, which borders Brazil, we identified culture-proven sporotrichosis in 9 cases across 7 households. Public health officials should coordinate cross-border One Health actions and institute context-specific interventions.
Sporotrichosis is an implantation mycosis caused by thermal-dimorphic fungi belonging to the Sporothrix schenckii complex (1). Among pathogenic species, S. brasiliensis has high virulence, epidemic potential, and zoonotic/enzootic transmission that occurs through bites, scratches, or contact with exudates from infected animals, particularly domestic cats (2–4).
In South America, S. brasiliensis was first identified in Brazil and has since been reported in other Latin America countries (1–8). Over recent decades, sporotrichosis in Brazil has seen a substantial epidemiologic shift, marked by intense, widespread urban zoonotic outbreaks, initially concentrated in Rio de Janeiro, affecting cats, dogs, and humans (2,9). Those outbreaks have spread to several cities in the southern and southeastern states, including Foz do Iguaçu, located on the Triple Frontier (Argentina, Brazil, and Parguay) between Argentina and Paraguay (2,3,5,7,10). Recently, a cat (Felis catus) infection by S. brasiliensis was reported in Ciudad del Este in Paraguay (8). In Argentina, the first human isolation of S. brasiliensis was documented in 1986 in the south of province of Misiones with no identified source of infection (4). Since then, zoonotic sporotrichosis cases have increased, and the central and southern regions of the country report most occurrences (1,4).
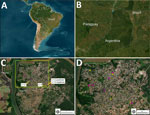
This study reports the emergence of urban transmission of feline sporotrichosis in Puerto Iguazú, Misiones, Argentina (25°36′39″S, 54°34′49″W). Located in the extreme northeast of Argentina, on the border of the Triple Frontier, the city has a population of ≈54,675 people and is 1,278 km from Buenos Aires. Puerto Iguazú is a major tourist destination because of the Iguazu Falls and is characterized by substantial cross-border dynamics, including high population and commercial movement.
During August 2023–February 2024, we conducted an intensified passive surveillance on 21 domestic cats (F. catus) from 12 households in the urban area of Puerto Iguazú (Figure). We included cats with lesions consistent with feline sporotrichosis (ulcers, scabs, soft nodules, and ulcerated subcutaneous nodules with exudate) and other cats without lesions but in contact with affected cats or living in areas with documented cases. No cats received treatment before sample collection. Pet owners provided written consent, and we recorded clinical, epidemiologic, and demographic data. Veterinarians evaluated all suspected cases and unaffected cats in contact with affected cats, and ongoing prevention and awareness campaigns provided information to owners and the community.
We collected nasal and lesion swab specimens from cats with skin lesions and nasal swabs from cats without lesions. We conducted diagnosis and species identification of Sporothrix by using phenotypic (Giemsa stain and culture) and genotypic methods (sequencing internal transcribed spacer region and partial sequencing of the calmodulin gene) (1,4,10).
We studied 21 cases. Nine (42.9%) were suspected cases, and 12 (57.1%) were unaffected cats. We confirmed feline sporotrichosis by culture in 77.8% (7/9) of the suspected cases and 16.7% (2/12) of the unaffected cats (Appendix Figure). We confirmed S. brasiliensis in 77.8% (7/9) cases by using molecular analysis. Two samples were inconclusive because of mold and bacterial contamination, which hindered identification of Sporothrix species (Table). Among the 2 confirmed cases in unaffected cats, we identified sneezing as the sole symptom in 1 case, and we ruled out 2 suspected cases because of differential diagnosis (dog bite and dermatophytosis) (Table). We reported all cases to health authorities.
We identified feline sporotrichosis cases in 58.3% (7/12) of the households. In 2 households, we detected multiple cases, suggesting intradomestic transmission. However, in 5 households, we found only 1 cat with sporotrichosis. Most of the cats had free access to streets, neighboring properties, and vacant lots. The average distance between the nearest households with feline sporotrichosis cases was 1.84 ± 1.22 km (range 0–4.54 km) (Table; Figure).
Our results describe the largest outbreak the S. brasiliensis in Argentina to date. We identified 9 proven cases of feline sporotrichosis in 7 months in Puerto Iguazú, in the province of Misiones, which is more than reported for the whole country (1). The outbreak reflects transmission dynamics similar to the epidemic in Brazil. Evidence shows multiple foci of transmission and asymptomatic carriers spreading the S. brasiliensis fungus (2,5,7,10). In addition, the nearest epidemic focus is on the Brazil side of the Triple Frontier (7), and to our knowledge, Buenos Aires and Santa Cruz reported the latest cases of feline sporotrichosis in Argentina (1).
Asymptomatic carriers hinder sporotrichosis control efforts by delaying diagnosis and treatment. Screening all contacts of confirmed cases is essential to minimize the risk for transmission (1,10). Addressing those challenges requires mandatory case reporting and public health measures. The detection and control of the expansion of feline sporotrichosis outside Brazil in contiguous countries requires coordinated cross-border One Health actions and context-specific interventions, which will be crucial to safeguard local communities and tourists (1,5).
Dr. Vizcaychipi is a professor of microbiology at Universidad del Salvador and a researcher at the Instituto Misionero de Biodiversidad and the Instituto Nacional de Medicina Tropical, Administración Nacional de Laboratorios e Institutos de Salud–“Carlos G. Malbrán,” Puerto Iguazú, Misiones, Argentina. Her research interests focus on emerging tropical zoonoses, including parasites and fungi, approached through a One Health framework.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Ministerio de Salud Pública (Misiones) and Instituto Misionero de Biodiversidad for support and collaboration, as well as Consejo de Veterinarios de Misiones, Zoonosis Iguazú, private veterinary clinics in Puerto Iguazú, the Sociedad Rural de Ganado Menor (Misiones), and all pet owners involved in the study for their trust and cooperation.
This study adhered to established ethical standards for veterinary research, ensuring the welfare and humane treatment of all animals involved. Sample collection was performed by qualified veterinarians using minimally invasive methods to reduce discomfort and stress. Procedures followed veterinary best practices and complied with international guidelines. Informed consent was obtained from all pet owners, who were briefed on the study objectives, methods, and potential benefits. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee and Institutional Commission for the Care and Use of Experimental Animals of the Faculty of Agricultural and Veterinary Sciences, Universidad del Salvador, Pilar, Provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina (ICCUEA06-2021), with permits for the collection of natural resources and/or genetic material granted by the Instituto Misionero de Biodiversidad, Puerto Iguazú, Misiones, Argentina, and the Ministerio de Ecología y Recursos Naturales (Misiones) Argentina (Expte. 9950-70-2023-1).
The strains were deposited in the culture collection of the Mycology Department at Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Administración Nacional de Laboratorios e Institutos de Salud, Buenos Aires, Argentina and in the Biobank of the Instituto Misionero de Biodiversidad, Puerto Iguazú, Misiones, Argentina (https://imibio.misiones.gob.ar/es). The data presented are part of a broader ongoing project, Proyecto SIGEVA-USAL 2022-2025, entitled Estudio eco-epidemiológico y sanitario de Sporothrix brasiliensis en localidades correntinas y misioneras del Corredor Jesuítico Guaraní Argentino.
References
- Etchecopaz A, Toscanini MA, Gisbert A, Mas J, Scarpa M, Iovannitti CA, et al. Sporothrix brasiliensis: a review of an emerging South American fungal pathogen, its related disease, presentation and spread in Argentina. J Fungi (Basel). 2021;7:170. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rodrigues AM, de Hoog GS, de Camargo ZP. Sporothrix species causing outbreaks in animals and humans driven by animal–animal transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12:
e1005638 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Rabello VBS, Almeida MA, Bernardes-Engemann AR, Almeida-Paes R, de Macedo PM, Zancopé-Oliveira RM. The historical burden of sporotrichosis in Brazil: a systematic review of cases reported from 1907 to 2020. Braz J Microbiol. 2022;53:231–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Córdoba S, Isla G, Szusz W, Vivot W, Hevia A, Davel G, et al. Molecular identification and susceptibility profile of Sporothrix schenckii sensu lato isolated in Argentina. Mycoses. 2018;61:441–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rossow JA, Queiroz-Telles F, Caceres DH, Beer KD, Jackson BR, Pereira JG, et al. A One Health approach to combatting Sporothrix brasiliensis: narrative review of an emerging zoonotic fungal pathogen in South America. J Fungi (Basel). 2020;6:247. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thomson P, González C, Blank O, Ramírez V, Río CD, Santibáñez S, et al. Sporotrichosis outbreak due to Sporothrix brasiliensis in domestic cats in Magallanes, Chile: a One-Health-approach study. J Fungi (Basel). 2023;9:226. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prado C, Chiyo L, Santi C, Cognialli R, Reis G, Geraldo M, et al. P464 feline sporotrichosis: an emerging disease in the Brazilian side of the Southern Triple Border. Med Mycol. 2022;60(suppl 1):myac072P464.
- do Prado CM, Razzolini E, Santacruz G, Ojeda L, Geraldo MR, Segovia N, et al. First cases of feline sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis in Paraguay. J Fungi (Basel). 2023;9:972. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ribeiro Dos Santos A, Misas E, Min B, Le N, Bagal UR, Parnell LA, et al. Emergence of zoonotic sporotrichosis in Brazil: a genomic epidemiology study. Lancet Microbe. 2024;5:e282–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cognialli RCR, Cáceres DH, Bastos FAGD, Cavassin FB, Lustosa BPR, Vicente VA, et al. Rising incidence of Sporothrix brasiliensis infections, Curitiba, Brazil, 2011–2022. Emerg Infect Dis. 2023;29:1330–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figures
Table
Suggested citation for this article: Vizcaychipi KA, López-Joffre MC, Martínez M, Cuéllar-Sáenz JA, Ramos M, Agüero C, et al. Emergence of feline sporotrichosis near Brazil border, Argentina, 2023–2024. Emerg Infect Dis. 2025 May [date cited]. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid3105.241882
Original Publication Date: April 22, 2025
Table of Contents – Volume 31, Number 5—May 2025
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Katherina A. Vizcaychipi, Rucci No. 56, N3370 Puerto Iguazú, Misiones, Argentina
Top