Volume 6, Number 1—February 2000
Dispatch
Molecular Typing of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Blockley Outbreak Isolates from Greece
Figure 1
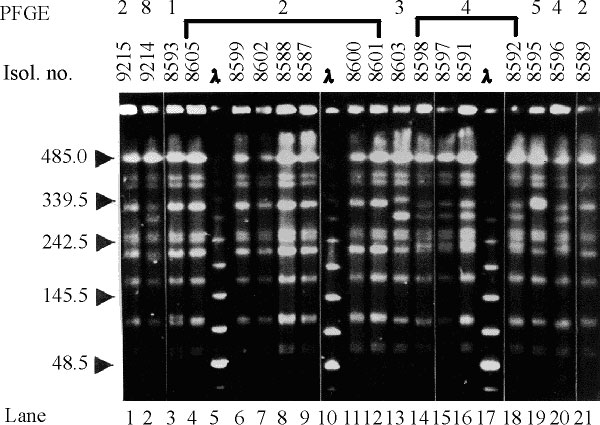
Figure 1. Sample pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) gel of representative Salmonella blockley isolates, indicating common and unique DNA fingerprints. Electrophoresis was through 1% agarose/0.5 x TBE, in a CHEF DRIII apparatus (BioRad Laboratories), at 14° C with a 120° switch angle and a run time of 20 hours, with a linear ramp of switching times from 5 to 32 seconds. Gels were stained with 0.5 mg/L ethidium bromide and documented under UV illumination by the EasyWin32 system (HeroLab, Germany). Images were assessed visually, and different PFGE subtypes (A1, A2, ...) were assigned to isolates with electrophoretic patterns differing by one to three DNA fragments (23). Gel images were also processed by the GelCompar software (Applied Maths, Kortrijk, Belgium), and on the basis of PFGE pattern similarities, a dendrogram was constructed by using the Dice coefficient and clustering by the unweighted pair group method, which uses arithmetic averages (UPGMA) with a 2% tolerance in band position difference. Isol. no.: isolate number. PFGE: subtypes of PFGE type A. The sizes, in kb, of lambda phage DNA concatamers (New England Biolabs) are shown to the left of the gel. All lanes are from the same gel.
References
- Fisher IST. on behalf of Enter-net participants. Enter-net Quarterly Salmonella Report - 98/3 (1998 Jul-Sep). Available from: URL: http://www2.phls.co.uk/reports/latest.htm
- Limawongpranee S, Hayashidani H, Okatani AT, Ono K, Hirota C, Kaneko K, Prevalence and persistence of Salmonella in broiler chicken flocks. J Vet Med Sci. 1999;61:255–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Matsushita S, Yamada S, Sekiguchi K, Kusunokui J, Ohta K, Kudoh Y. Serovar-distribution and drug-resistance of Salmonella strains isolated from domestic and imported cases in 1990-1994 in Tokyo. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1996;70:42–50.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yasin RM, Jegathesan MM, Tiew CC. Salmonella serotypes isolated in Malaysia over the ten-year period 1983-1992. Asia Pac J Public Health. 1996-97;9:1–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rusul G, Khair J, Radu S, Cheah CT, Yassin RM. Prevalence of Salmonella in broilers at retail outlets, processing plants and farms in Malaysia. Int J Food Microbiol. 1996;33:183–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sasipreeyajan J, Jerngklinchan J, Koowatananukul C, Saitanu K. Prevalence of salmonellae in broiler, layer and breeder flocks in Thailand. Trop Anim Health Prod. 1996;28:174–80.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Morse LJ, Rubenstein AD. A food-borne institutional outbreak of enteritis due to Salmonella blockley. JAMA. 1967;202:939–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Albert S, Weber B, Schafer V, Rosenthal P, Simonsohn M, Doerr HW. Six enteropathogens from a case of acute gastroenteritis. Infection. 1990;18:381–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Duijkeren E, Sloet van Oldruitenborgh-Oosterbaan MM, Houwers DJ, van Leeuwen WJ, Kalsbeek HC. Equine salmonellosis in a Dutch veterinary teaching hospital. Vet Rec. 1994;135:248–50.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mallaret MR, Turquand O, Blatier JF, Croize J, Gledel J, Micoud M, Human salmonellosis and turtles in France. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 1990;38:71–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Levre E, Valentini P, Brunetti M, Sacchelli F. Stationary and migratory avifauna as reservoirs of Salmonella, Yersinia and Campylobacter. Ann Ig. 1989;1:729–40.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Morinigo MA, Cornax R, Castro D, Jimenez-Notaro M, Romero P, Borrego JJ. Antibiotic resistance of Salmonella strains isolated from natural polluted waters. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990;68:297–302.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Garcia-Villanova Ruiz B, Cueto Espinar A, Bolanos Carmona MJ. A comparative study of strains of salmonella isolated from irrigation waters, vegetables and human infections. Epidemiol Infect. 1987;98:271–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Matsushita S, Yamada S, Inaba M, Kusunoki J, Kudoh Y, Ohashi M. Serovar distribution and drug resistance of Salmonella isolated from imported and domestic cases in 1980-1989 in Tokyo. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1992;66:327–39.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bangtrakulobth A, Suthienkul O, Kitjakara A, Pornrungwong S, Siripanichgon K. First isolation of Salmonella blockley in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1994;25:688–92.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Atanassova V, Matthes S, Muhlbauer E, Helmuth R, Schroeter A, Ellendorff F. Plasmid profiles of different Salmonella serovars from poultry flocks in Germany. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1993;106:404–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hamouda O. Outbreak of Salmonella blockley infections in Germanypreliminary investigation results. Eurosurveillance Weekly 1998;2:980924. Available at URL: http://www.eurosurv.org/1998/980924.htm
- Benons L. Salmonella blockley infections in England and Wales, 1998. Eurosurveillance Weekly 1998;2:980924. Available at URL: http://www.eurosurv.org/1998/980924.htm
- Vassilogiannakopoulos A, Tassios P, Lampiri M. Salmonella blockley infection in Greece. Eurosurveillance Weekly 1999;3:990408. Available at URL: http://www.eurosurv.org/1999/990408.htm
- Kauffman F. Serological diagnosis of Salmonella species. Copenhagen (Denmark): Munksgaard; 1972.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically. Approved Standard M7-A2. Wayne (PA): The Committee; 1997.
- Tassios PT, Vatopoulos AC, Mainas E, Gennimata D, Papadakis J, Tsiftsoglou A, Molecular analysis of ampicillin-resistant sporadic Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi B clinical isolates. Clin Microbiol Infect. 1997;3:317–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV, Mickelsen PA, Murray BE, Persing DH, Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:2233–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tassios PT, Markogiannakis A, Vatopoulos AC, Katsanikou E, Velonakis EN, Kourea-Kremastinou K, Molecular epidemiology of antibiotic resistance of Salmonella enteritidis during a 7-year period in Greece. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:1316–21.PubMedGoogle Scholar