Volume 7, Number 3—June 2001
Perspective
Seasonal Variation in Host Susceptibility and Cycles of Certain Infectious Diseases
Figure 2
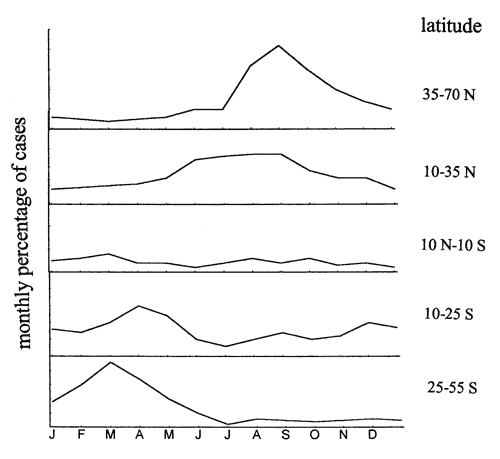
Figure 2. . Seasonal variation in the incidence of poliomyelitis by latitude, 1956-57. As distance from the equator increases, a higher proportion of cases are evident in summer and fall months. Adapted from reference 9.
References
- Brownlee J. An investigation into the periodicity of measles epidemics in London from 1703 to the present day by the method of the periodogram. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London 1918;B 208:225-50.
- Anderson RM, Grenfell BT, May RM. Oscillatory fluctuations in the incidence of infectious disease and the impact of vaccination: time series analysis. J Hyg Camb. 1984;93:587–608. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Riedo FX, Plikaytis B, Broome C. Epidemiology and prevention of meningococcal disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1995;14:643–57. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Witte JJ, Karchmer A, Case M, Herrmann KL, Abrutyn E, Kassanoff I, Epidemiology of rubella. Am J Dis Child. 1969;118:107–11.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Török TJ, Kilgore PE, Clarke MJ, Holman RC, Bresee JS, Glass RI. Visualizing geographic and temporal trends in rotavirus activity in the United States, 1991 to 1996. National Respiratory and Enteric Virus Surveillance System Collaborating Laboratories. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1997;16:941–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: Influenza activity--United States, 1999-2000 season. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2000;49:173–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: Influenza activity--United States and worldwide, 1995-96 season, and composition of the 1996-97 influenza vaccine. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1996;45:326–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dowell SF, Whitney C, Wright C, Schuchat A. Seasonal changes in invasive pneumococcal disease. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001. In press.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Paccaud MF. World trends in poliomyelitis morbidity and mortality, 1951-1975. World Health Stat Q. 1979;32:198–224.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cook SM, Glass R, LeBaron C, Ho M-S. Global seasonality of rotavirus infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1990;68:171–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hope-Simpson RE, Golubev D. A new concept of the epidemic process of influenza A virus. Epidemiol Infect. 1987;99:5–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Blakebrough IS, Greenwood B, Whittle H, Bradley A, Gilles H. The epidemiology of infections due to Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria lactamica in a northern Nigerian community. J Infect Dis. 1982;146:626–37. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Update: respiratory syncytial virus activity - United States, 1998-1999 Season. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1999;48:1104–15.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kohn MA, Farley T, Sundin D, Tapia R, McFarland L, Arden N. Three summertime outbreaks of influenza type A. J Infect Dis. 1995;172:246–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Langmuir AD, Schoenbaum S. The epidemiology of influenza. Hosp Pract. 1976;11:49–56.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hammond GW, Raddatz R, Gelskey D. Impact of atmospheric dispersion and transport of viral aerosols on the epidemiology of influenza. Rev Infect Dis. 1989;11:494–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kim PE, Musher D, Glezen W, Rodriguez-Barradas M, Nahm W, Wright C. Association of invasive pneumococcal disease with season, atmospheric conditions, air pollution, and the isolation of respiratory viruses. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22:100–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Checkley W, Epstein L, Gilman R, Figueroa D, Cama RI, Patz JA. Effects of El Niño and ambient temperature on hospital admissions for diarrheal diseases in Peruvian children. Lancet. 2000;355:442–50.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chew FT, Doraisingham S, Ling A, Kumarasinghe G, Lee B. Seasonal trends of viral respiratory tract infections in the tropics. Epidemiol Infect. 1998;121:121–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sung RY, Murray H, Chan R, Davies D, French G. Seasonal patterns of respiratory syncytial virus infection in Hong Kong: a preliminary report. J Infect Dis. 1987;156:527–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nathanson N, Martin J. The epidemiology of poliomyelitis: enigmas surrounding its appearance, epidemicity, and disappearance. Am J Epidemiol. 1979;110:672–92.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Greenwood B. The epidemiology of acute bacterial meningitis in tropical Africa. Bacterial Meningitis. London: Academic Press; 1987. p. 61-91.
- Greenwood BM, Blakebrough I, Bradley A, Wali S, Whittle H. Meningococcal disease and season in sub-Saharan Africa. Lancet. 1984;i:1339–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Diermayer M, Hedberg K, Hoesly F, Fischer M, Perkins B, Reeves M, Epidemic serogroup B meningococcal disease in Oregon: the evolving epidemiology of the ET-5 strain. JAMA. 1999;281:1493–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- D'Alessio D, Minor T, Allen C, Tsiatis A, Nelson D. A study of the proportions of swimmers among well controls and children with enterovirus-like illness shedding or not shedding an enterovirus. Am J Epidemiol. 1981;113:533–41.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hawley HB, Morin D, Geraghty M, Tomkow J, Phillips C. Coxsackievirus B epidemic at a boys' summer camp: isolation of virus from swimming water. JAMA. 1973;226:33–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hamer W. Epidemic disease in England--the evidence of variability and persistency of type. Lancet. 1906;11:733–9.
- Fine PE, Clarkson J. Measles in England and Wales - I: an analysis of factors underlying seasonal patterns. Int J Epidemiol. 1982;11:5–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rojansky N, Brzezinski A, Schenker J. Seasonality in human reproduction: an update. Hum Reprod. 1992;7:735–45.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wehr TA, Moul D, Barbato G, Giesen HA, Seidel JA, Barker C, Conservation of photoperiod-responsive mechanisms in humans. Am J Physiol. 1993;265:R846–57.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Carlson LL, Zimmermann A, Lynch G. Geographic differences for delay of sexual maturation in Peromyscus leukopus: effects of photoperiod, pinealectomy, and melatonin. Biol Reprod. 1989;41:1004–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lincoln GA. Reproductive seasonality and maturation throughout the complete life-cycle in the mouflon ram (ovis musimon). Anim Reprod Sci. 1998;53:87–105. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rhind SM, McMillen S, Duff E, Hirst D, Wright S. Seasonality of meal patterns and hormonal correlates in red deer. Physiol Behav. 1998;65:295–302. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Herndon JG, Bein M, Nordmeyer D, Turner J. Seasonal testicular function in male rhesus monkeys. Horm Behav. 1996;30:266–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chan PJ, Hutz R, Dukelow W. Nonhuman primate in vitro fertilization: seasonality, cumulus cells, cyclic nucleotides, ribonucleic acid, and viability assays. Fertil Steril. 1982;38:609–15.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Löscher W, Fiedler M. The role of technical, biological and pharmacological factors in the laboratory evaluation of anticonvulsant drugs. VI. Seasonal influences on maximal electroshock and pentylentetrazol seizure thresholds. Epilepsy Res. 1996;25:3–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sargeant JM, Shoukri M, Martin S, Leslie K, Lissemore K. Investigating potential risk factors for seasonal variation: an example using graphical and spectral analysis methods based on the production of milk components in dairy cattle. Prev Vet Med. 1998;36:167–78. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yellon SM, Fagoaga O, Nehlsen-Cannarella S. Influence of photoperiod on immune cell functions in the male Siberian hamster. Am J Physiol. 1999;276:R97–102.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Demas GE, Nelson R. Exogenous melatonin enhances cell-mediated, but not humoral, immune function in adult male deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus). J Biol Rhythms. 1998;13:245–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Feigin RD, San Joaquin VH, Haymond MW, Wyatt RG. Daily periodicity of susceptibility of mice to pneumococcal infection. Nature. 1969;224:379–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shackelford PG, Feigin RD. Periodicity of susceptibility to pneumococcal infection: influence of light and adrenocortical secretions. Science. 1973;182:285–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wongwiwat M, Sukapanit S, Triyanond C, Sawyer WD. Circadian rhythm of the resistance of mice to acute pneumococcal infection. Infect Immun. 1972;5:442–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sack RL, Brandes R, Kendall A, Lewy A. Entrainment of free-running circadian rhythms by melatonin in blind people. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1070–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sher L, Goldman D, Ozaki N, Rosenthal N. The role of genetic factors in the etiology of seasonal affective disorder. J Affect Disord. 1999;53:203–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Eastman CI, Young M, Fogg L, Liu L, Meaden P. Bright light treatment of winter depression: a placebo-controlled trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55:883–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pell JP, Cobbe S. Seasonal variations in coronary heart disease. QJM. 1999;92:689–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ownby HE, Frederick J, Mortensen R, Ownby D, Russo J. Seasonal variations in tumor size at diagnosis and immunological responses in human breast cancer. Invasion Metastasis. 1986;6:246–56.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Calvo JR, Rafil-El-Idrissi M, Pozo D, Guerrero J. Immunomodulatory role of melatonin: specific binding sites in human and rodent lymphoid cells. J Pineal Res. 1995;18:119–26. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Boctor FN, Charmy R, Cooper E. Seasonal differences in the rhythmicity of human male and female lymphocyte blastogenic responses. Immunol Invest. 1989;18:775–84. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maes M, Stevens W, Scharpe S, Bosmans E, De Meyer F, D'Hondt P, Seasonal variation in peripheral blood leukocyte subsets and in serum interleukin-6, and soluble interleukin-2 and -6 receptor concentrations in normal volunteers. Experientia. 1994;50:821–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nelson RJ, Drazen D. Melatonin mediates seasonal adjustments in immune function. Reprod Nutr Dev. 1999;39:383–98. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Paigen B, Ward E, Reilly A, Houten L, Gurtoo HL, Minowada J, Seasonal variation of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in human lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1981;41:2757–61.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shadrin AS, Marinich I, Taros L. Experimental and epidemiological estimation of seasonal and climato-geographical features of non-specific resistance of the organism to influenza. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21:155–61.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schulman JL, Kilbourne E. Experimental transmission of influenza virus infection in mice. II. Some factors affecting the incidence of transmitted infections. J Exp Med. 1963;118:267–75. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Swartz TA, Skalska P, Gerichter C. Routine administration of oral polio vaccine in a subtropical area. Factors possibly influencing sero-conversion rates. J Hyg Camb. 1972;70:719–26. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization Collaborative Study Group on Oral Poliovirus V. Factors affecting the immunogenicity of oral poliovirus vaccine: a prospective evaluation in Brazil and the Gambia. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:1097–106.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Deming MS, Linkins R, Jaitch K, Hull H. The clinical efficacy of trivalent oral polio vaccine in the Gambia by season of vaccine administration. J Infect Dis. 1997;175(suppl1):S254–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schonberger LB, McGowan JJ, Gregg M. Vaccine-associated poliomyelitis in the United States, 1961-1972. Am J Epidemiol. 1976;104:202–11.PubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: April 26, 2012
Page updated: April 26, 2012
Page reviewed: April 26, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.