Volume 8, Number 12—December 2002
Research
Use of Binary Cumulative Sums and Moving Averages in Nosocomial Infection Cluster Detection1
Figure 1
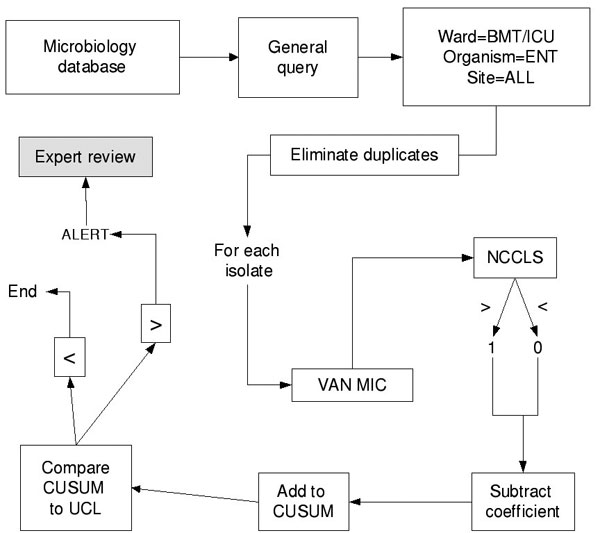
Figure 1. Data processing methodology for cumulative sums. BMT, bone marrow transplant unit; ICU, intensive care unit; ENT, enterococcus; VAN MIC, vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration; NCCLS, National Committee on Laboratory Standards antibiotic susceptibility breakpoint; CUSUM, cumulative sum; UCL, upper confidence limit.
1 Portions of this research were presented at the 39th Annual Meeting of the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), San Francisco, California, USA, October 25–28, 2001.
Page created: July 19, 2010
Page updated: July 19, 2010
Page reviewed: July 19, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.