Volume 8, Number 9—September 2002
Research
Characterization of Flagella Produced by Clinical Strains of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Figure 3
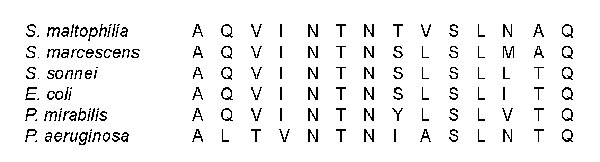
Figure 3. N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis. The first 14 residues of SMFliC showed considerable identity to other flagellins. The highest degree of identity was found with the Serratia marcescens flagellin (78.6%). Stenotrophomonas maltophilia flagellin also showed identity to flagellins of Shigella sonnei, Escherichia coli, and Proteus mirabilis (71.4%), and the lowest identity was found with Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagellin (57.2%). The numbers on top indicate the amino acid position.
Page created: July 16, 2010
Page updated: July 16, 2010
Page reviewed: July 16, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.