Volume 12, Number 11—November 2006
Research
Spatiotemporal Analysis of Invasive Meningococcal Disease, Germany
Figure 2
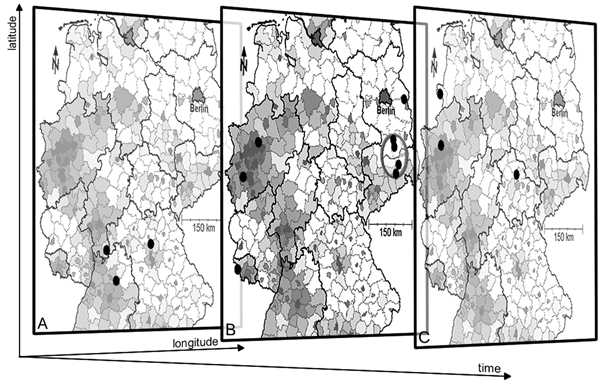
Figure 2. Retrospective identification of a cluster (cluster 10) of the finetype C:P1.5,2:F3–3 in 3 temporal planes using SaTScan (11). Planes A, B, and C represent consecutive temporal windows of 30 days in 2003. Cases with the finetype in question are shown by dark ovals defined by the dimensions longitude, latitude, and time. Although planes A and C do not show spatial clustering, plane B shows an accumulation of 4 cases in 2 counties within a circle encompassing a population of 339,185 (radius 28.78 km, p = 0.004; marked by a gray oval). Counties of Germany are shaded according to their population density (darker indicates a higher population density).
References
- Maiden MC, Bygraves JA, Feil E, Morelli G, Russell JE, Urwin R, Multilocus sequence typing: a portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:3140–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Russell JE, Jolley KA, Feavers IM, Maiden MC, Suker J. PorA variable regions of Neisseria meningitidis. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:674–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Thompson EA, Feavers IM, Maiden MC. Antigenic diversity of meningococcal enterobactin receptor FetA, a vaccine component. Microbiology. 2003;149:1849–58. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cooke RP, Riordan T, Jones DM, Painter MJ. Secondary cases of meningococcal infection among close family and household contacts in England and Wales, 1984–7. BMJ. 1989;298:555–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Olivares R, Hubert B. Clusters of meningococcal disease in France (1987–1988). Eur J Epidemiol. 1992;8:737–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jackson LA, Schuchat A, Reeves MW, Wenger JD. Serogroup C meningococcal outbreaks in the United States. An emerging threat. JAMA. 1995;273:383–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Le Guerrier P, Pilon P, Sauvageau C, Deshaies D. Spatio-temporal cluster of cases of invasive group B Neisseria meningitidis infections on the island of Montreal. Can Commun Dis Rep. 1997;23:25–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Farrington CP, Beale AD. The detection of outbreaks of infectious diseases. In: Gierl L, Cliff AD, Valleron AJ, Farrington CP, Bull M, editors. Proceedings of the International Workshop on Geomedical Systems. Leipzig (Germany): Teubner BG; 1998. p. 97–117.
- Ranta J, Makela PH, Arjas E. Predicting meningococcal disease outbreaks in structured populations. Stat Med. 2004;23:927–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hoebe CJ, de Melker H, Spanjaard L, Dankert J, Nagelkerke N. Space-time cluster analysis of invasive meningococcal disease. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:1621–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kulldorff M. A spatial scan statistic. Comm Statist Theory Methods. 1997;26:1481–96. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Sauders BD, Fortes ED, Morse DL, Dumas N, Kiehlbauch JA, Schukken Y, Molecular subtyping to detect human listeriosis clusters. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:672–80.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tirabassi MV, Wadie G, Moriarty KP, Garb J, Konefal SH, Courtney RA, Geographic information system localization of community-acquired MRSA soft tissue abscesses. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40:962–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jennings JM, Curriero FC, Celentano D, Ellen JM. Geographic identification of high gonorrhea transmission areas in Baltimore, Maryland. Am J Epidemiol. 2005;161:73–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mostashari F, Kulldorff M, Hartman JJ, Miller JR, Kulasekera V. Dead bird clusters as an early warning system for West Nile virus activity. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:641–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cousens S, Smith PG, Ward H, Everington D, Knight RS, Zeidler M, Geographical distribution of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Great Britain, 1994–2000. Lancet. 2001;357:1002–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Norstrom M, Pfeiffer DU, Jarp J. A space-time cluster investigation of an outbreak of acute respiratory disease in Norwegian cattle herds. Prev Vet Med. 1999;47:107–19. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Andrade AL, Silva SA, Martelli CM, Oliveira RM, Morais Neto OL, Siqueira JB Jr, Population-based surveillance of pediatric pneumonia: use of spatial analysis in an urban area of Central Brazil. Cad Saude Publica. 2004;20:411–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yih WK, Caldwell B, Harmon R, Kleinman K, Lazarus R, Nelson A, National Bioterrorism Syndromic Surveillance Demonstration Program. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2004;53(Suppl):43–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dreesman J, Scharlach H. Spatial-statistical analysis of infectious disease notification data in Lower Saxony. Gesundheitswesen. 2004;66:783–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kulldorff M, Heffernan R, Hartman J, Assuncao R, Mostashari F. A space-time permutation scan statistic for disease outbreak detection. PLoS Med. 2005;2:e59. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schrauder A, Claus H, Elias J, Vogel U, Haas W, Hellenbrand W. Capture-recapture analysis to estimate the incidence of invasive meningococcal disease in Germany, 2003. [Epublished]. Epidemiol Infect. 2006. In press.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vogel U, Claus H, Frosch M. Capsular operons. In: Pollard AJ, Maiden MC, editors. Meningococcal disease: methods and protocols. Totowa (NJ): Humana Press; 2001. p. 187–201.
- Hunter PR, Gaston MA. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: an application of Simpson's index of diversity. J Clin Microbiol. 1988;26:2465–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Grundmann H, Hori S, Tanner G. Determining confidence intervals when measuring genetic diversity and the discriminatory abilities of typing methods for microorganisms. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:4190–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vogel U, Claus H, von Müller L, Bunjes D, Elias J, Frosch M. Bacteremia in an immunocompromised patient caused by a commensal Neisseria meningitidis strain harboring the capsule null locus (cnl). J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:2898–901. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Harrison LH, Jolley KA, Shutt KA, Marsh JW, O'Leary M, Sanza LT, Antigenic shift and increased incidence of meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:1266–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van der Ende A, Hopman CT, Keijzers WC, Spanjaard L, Lodder EB, van Keulen PH, Outbreak of meningococcal disease caused by PorA-deficient meningococci. J Infect Dis. 2003;187:869–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hastings L, Stuart J, Andrews N, Begg N. A retrospective survey of clusters of meningococcal disease in England and Wales, 1993 to 1995: estimated risks of further cases in household and educational settings. Commun Dis Rep CDR Rev. 1997;7:R195–200.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zangwill KM, Schuchat A, Riedo FX, Pinner RW, Koo DT, Reeves MW, School-based clusters of meningococcal disease in the United States. Descriptive epidemiology and a case-control analysis. JAMA. 1997;277:389–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hautmann W, Harms I, Vogel U, Zirngibl A, Wildner M. Cluster of meningococcal diseases in Allgaeu: strategies for intervention. Gesundheitswesen. 2005;67:853–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Block C, Roitman M, Bogokowsky B, Meizlin S, Slater PE. Forty years of meningococcal disease in Israel: 1951–1990. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;17:126–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Davison KL, Andrews N, White JM, Ramsay ME, Crowcroft NS, Rushdy AA, Clusters of meningococcal disease in school and preschool settings in England and Wales: What is the risk? Arch Dis Child. 2004;89:256–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mellmann A, Friedrich AW, Rosenkotter N, Rothganger J, Karch H, Reintjes R, Automated DNA sequence-based early warning system for the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus outbreaks. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: October 17, 2011
Page updated: October 17, 2011
Page reviewed: October 17, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.