Volume 24, Number 2—February 2018
Dispatch
Emergomyces africanus in Soil, South Africa
Figure 1
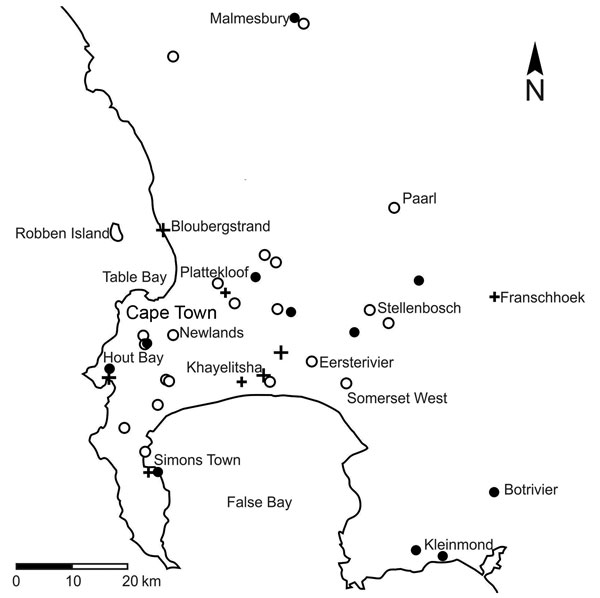
Figure 1. Results of molecular tests for the presence of Emergomyces africanus in soil samples in relation to residential locations of 14 patients diagnosed with emergomycosis (6), Cape Peninsula, Western Cape Province, South Africa. Black circles indicate Es. africanus detected in soil sample; white circles indicate Es. africanus not detected in soil sample; plus signs indicate residential locations of patients with emergomycosis. A larger cross indicates >1 infected patient at that particular location.
References
- Dukik K, Muñoz JF, Jiang Y, Feng P, Sigler L, Stielow JB, et al. Novel taxa of thermally dimorphic systemic pathogens in the Ajellomycetaceae (Onygenales). Mycoses. 2017;60:296–309. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schwartz IS, Kenyon C, Feng P, Govender NP, Dukik K, Sigler L, et al. 50 years of Emmonsia disease in humans: the dramatic emergence of a cluster of novel fungal pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1005198. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Maphanga TG, Britz E, Zulu TG, Mpembe RS, Naicker SD, Schwartz IS, et al. In vitro antifungal susceptibility of the yeast- and mould-phases of the dimorphic fungal pathogen, Emergomyces africanus (formerly Emmonsia species), from HIV-infected South African patients. J Clin Microbiol. 2017;55:1812–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schwartz IS, Govender NP, Corcoran C, Dlamini S, Prozesky H, Burton R, et al. Clinical characteristics, diagnosis, management and outcomes of disseminated emmonsiosis: a retrospective case series. Clin Infect Dis. 2015;61:1004–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ, editors. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. New York: Academic Press, Inc.; 1990. p. 315–22.
- Schwartz IS, Kenyon C, Lehloenya R, Claasens S, Spengane Z, Prozesky H, et al. AIDS-related endemic mycoses in Western Cape, South Africa, and clinical mimics: a cross-sectional study of adults with advanced HIV and recent-onset, widespread skin lesions. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017;4:ofx186. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Larsh HW, Hinton A, Furcolow ML. Laboratory studies of Histoplasma capsulatum. III. Efficiency of the flotation method in isolation of Histoplasma capsulatum from soil. J Lab Clin Med. 1953;41:478–85.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Emmons CW. The isolation from soil of fungi which cause disease in man. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1951;14(1 Series II):51–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kenyon C, Bonorchis K, Corcoran C, Meintjes G, Locketz M, Lehloenya R, et al. A dimorphic fungus causing disseminated infection in South Africa. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1416–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stewart R, Meyer K. Isolation of Coccidioides immitis (Stiles) from the soil. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1932;29:937–8. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Li Z, Chaturvedi V. The powers and perils of PCR in the search for the natural reservoirs of Coccidioides species. Mycopathologia. 2017;182:435–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: January 17, 2018
Page updated: January 17, 2018
Page reviewed: January 17, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.