Volume 24, Number 3—March 2018
Research
Capsule Typing of Haemophilus influenzae by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry1
Figure 3
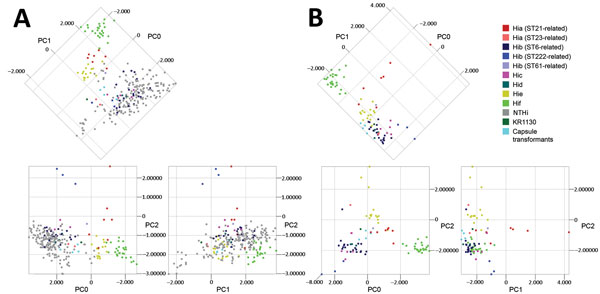
Figure 3. Principal component analysis (PCA) of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectra of encapsulated and nonencapsulated Haemophilus influenzae. A) PCA of all isolates (n = 258) of H. influenzae in the evaluation set representing all capsule types, which are color-coded according to capsule type and for Hia and Hib isolates by genetic lineage as shown by multilocus sequence typing (MLST) and capsule transformants (n = 4). The first 3 principal components (PC0, PC1, and PC2) are shown in 2-dimensional plots. Analysis showed the diversity of nontypeable H. influenzae (NTHi). Encapsulated isolates showed discrete clustering, which was further evaluated by PCA of encapsulated isolates separately. B) PCA of encapsulated isolates in the evaluation set (n = 83) and capsule transformants (n = 4) presented and color-coded as in panel A. Clustering of isolates on the basis of capsule type was evident, particularly for Hib, Hie, and Hif isolates. Different genetic lineages of the same capsule type (Hia and Hib) clustered separately. KR1130 (with a pseudogene type f cap locus) did not cluster with the other Hif isolates. Capsule transformants clustered together in proximity of Hid isolates, and not with their respective capsule type. Hia, H. influenzae type a; Hib, H. influenzae type b; Hic, H. influenzae type c; Hid, H. influenzae type d; Hie, H. influenzae type e; Hif, H. influenzae type f; ST, sequence type.
1Preliminary results from this study were presented at the IDWeek 2016 Conference, October 26−30, 2016, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.