Volume 26, Number 9—September 2020
Research
Isolation, Sequence, Infectivity, and Replication Kinetics of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Figure 3
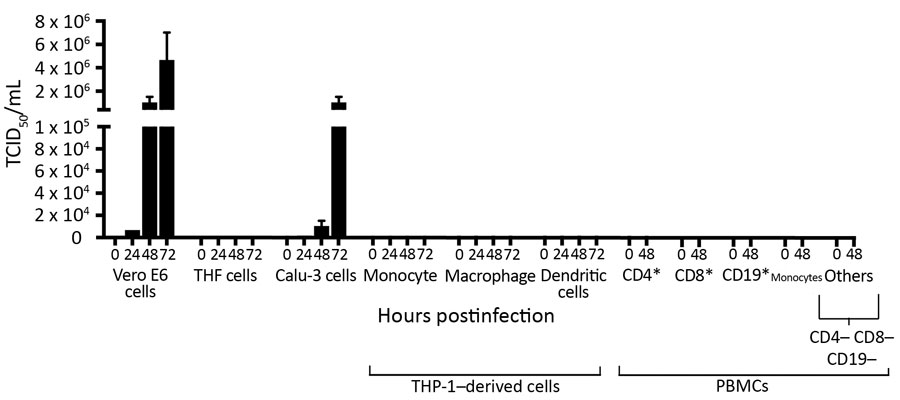
Figure 3. Replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in human structural and immune cells. To identify human cells that support SARS-CoV-2 replication, we infected human cell lines and primary cells at a multiplicity of infection of 0.01 (n = 2 independent experiments; supernatant from each experiment was titrated in triplicate). We infected Vero E6 cells as a control. THF (human telomerase life-extended cells) and Calu-3 cells (human lung adenocarcinoma–derived) cells represent human structural cells. THP-1 is a monocyte cell line that was used to derive macrophages and dendritic cells. PBMCs from 2 healthy human donors were used to generate CD4+, CD8+, CD19+, monocytes, and other (CD4–, CD8–, CD19–) cell populations. Supernatant from infected cells was collected at various times and titrated on Vero E6 cells to determine virus titers (TCID50). PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; TCID50, 50% tissue culture infectious dose.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.