Volume 27, Number 3—March 2021
Research
Daily Forecasting of Regional Epidemics of Coronavirus Disease with Bayesian Uncertainty Quantification, United States
Figure 2
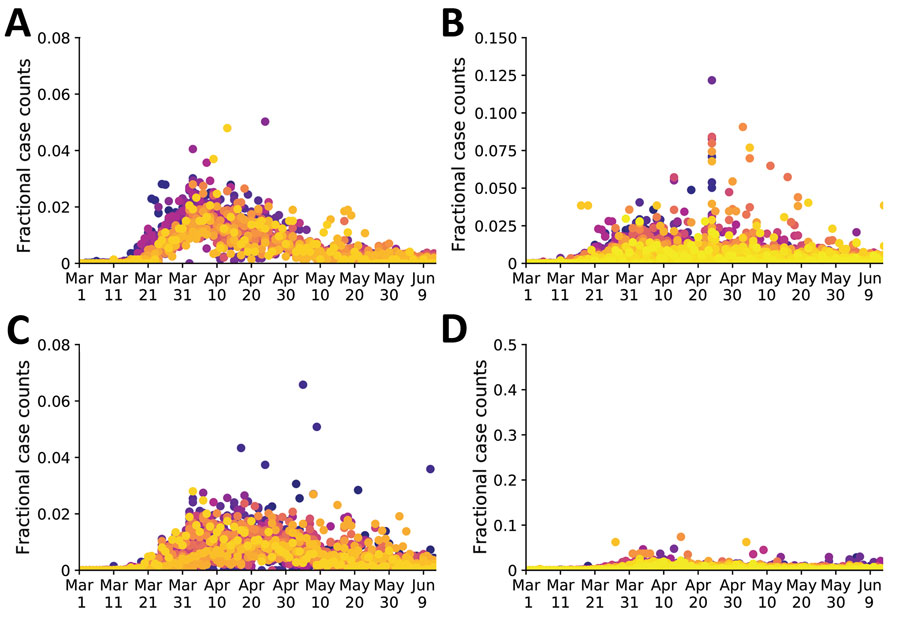
Figure 2. Temporal correlations of fractional case counts of coronavirus disease in and around the New York City, New York, metropolitan statistical area, United States, March 1–June 13, 2020. The fractional case count for a county on a given date is defined as the reported number of cases on that date divided by the total reported number of cases in the county over the entire time period of interest. Panels show the fractional cast counts for: A) the 23 counties comprising the New York City metropolitan statistical area (Fano factor 0.0026); B) the 62 counties comprising New York state (Fano factor 0.021); C) the 21 counties comprising New Jersey (Fano factor 1.2); and D) the 67 counties comprising Pennsylvania (Fano factor 0.028). Within each plot, different colors indicate the data points from each distinct county. Purple–yellow gradient indicates alphabetical order of the counties. A smaller Fano factor indicates less county-to-county variability.