Volume 30, Number 10—October 2024
Dispatch
Dengue Virus Serotype 3 Origins and Genetic Dynamics, Jamaica
Figure 2
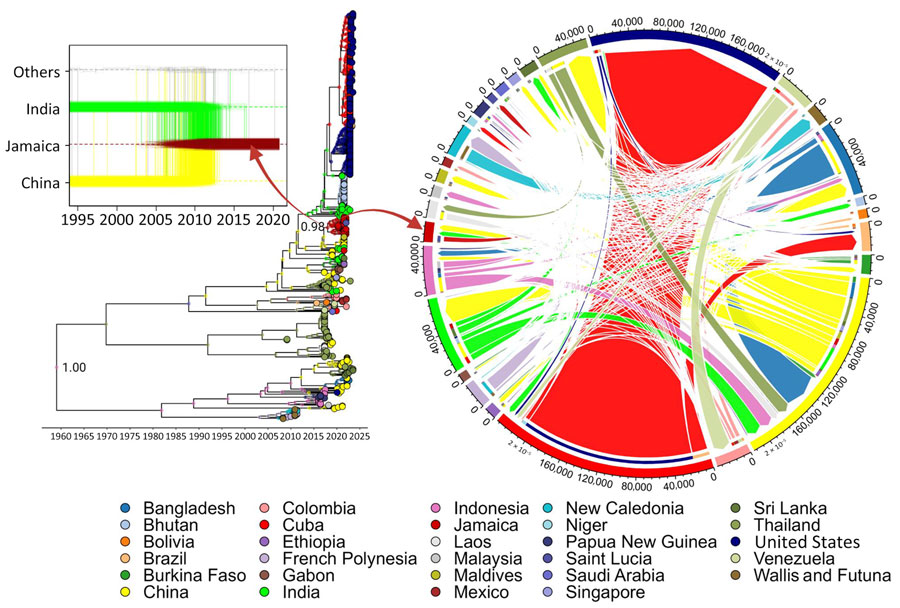
Figure 2. Time-scaled explicit discrete phylogeographic analysis of dengue virus serotype 3 (DENV-3) spread in Jamaica. Relationship between the dispersal trajectory of DENV-3 in the maximum clade credibility tree and the specific DENV-3 migration patterns into Jamaica over time (box) is indicated. Nodes of the tree represent the inferred country of origin for sampled strains. Arrows indicate the nodes from which taxa were selected for analysis by using the TaxaMarkovJumpHistoryAnalyzer (https://github.com/beast-dev/beast-mcmc). Only values of discrete state probability for the root and the node of interest are shown in the tree; complete state probability values of the nodes are indicated in Appendix Figure 2, panel B. Dynamic pathways of DENV-3 geographic movement are indicated by Markov jump mappings (right circular map). Transmission network of DENV-3 is summarized by Markov jump events, analyzed using TreeMarkovJumpHistoryAnalyzer and visualized in a circular layout by using the circlize package in R (The R Project for Statistical Computing, https://www.r-project.org). The width of each link reflects the frequency of virus movement; quantitative estimates were provided by using the TreeMarkovJumpHistoryAnalyzer. Tick marks on the outside of the circle’s segments indicate virus movement frequencies.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.