Volume 30, Number 11—November 2024
Research Letter
Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Resilience in Milk after Thermal Inactivation
Figure 2
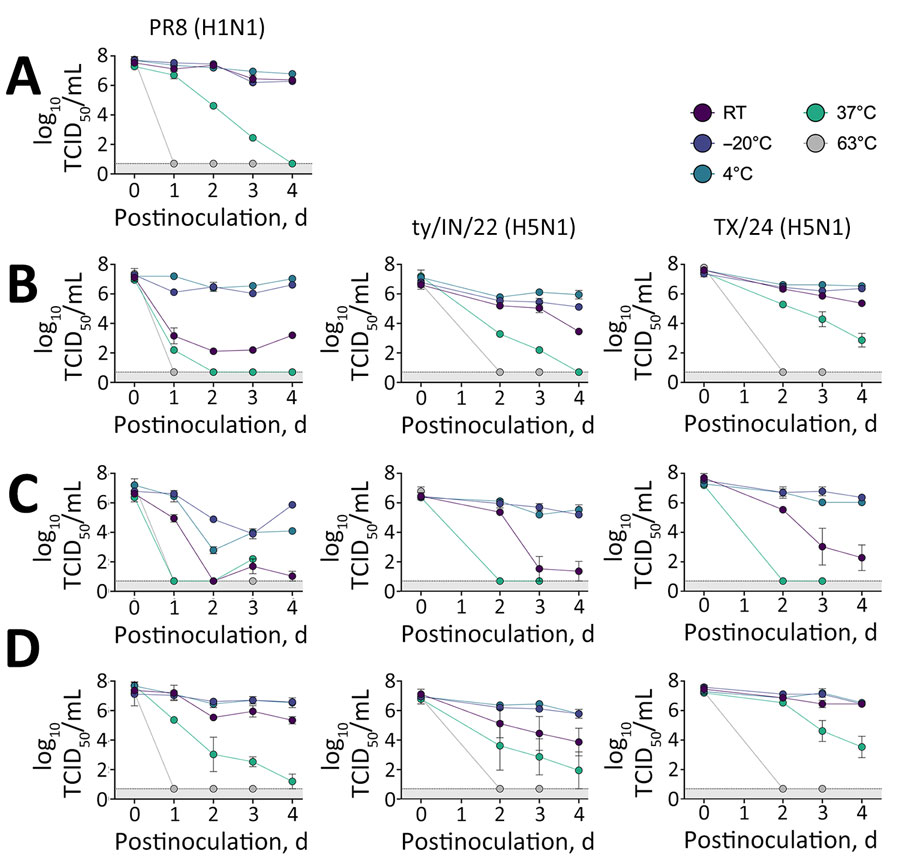
Figure 2. Stability of influenza A in retail and unpasteurized milk. We diluted influenza A viruses in either Opti-Mem control media (Fisher Scientific, https://www.fishersci.com) (A), retail off-the-shelf pasteurized whole milk (B), or 2 different sources of unpasteurized milk: colostrum milk (C) or mature milk (D). We then incubated 200-μL samples for several days at various temperatures, as shown. We subsequently titrated samples by TCID50 in MDCK cells. We tested 3 strains: PR8 (H1N1), ty/IN/22 (H5N1), and the reverse genetics version of TX/24 (H5N1). Unpasteurized colostrum milk produced during the first few days after birth contains high levels of immunoglobulins and antimicrobial peptides that might have had an effect in decreasing virus survival. PR8 (H1N1), wild-type strain A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 (H1N1); RT, room temperature; TCID50, 50% tissue culture infectious dose; TX/24, wild-type strain A/Texas/37/2024 (H5N1); ty/IN/22, wild-type highly pathogenic strain A/turkey/Indiana/3707-003/2022 (H5N1).