Volume 30, Number 8—August 2024
Dispatch
Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infections among Children before and during COVID-19 Pandemic, Taiwan, 2017–2023
Figure 1
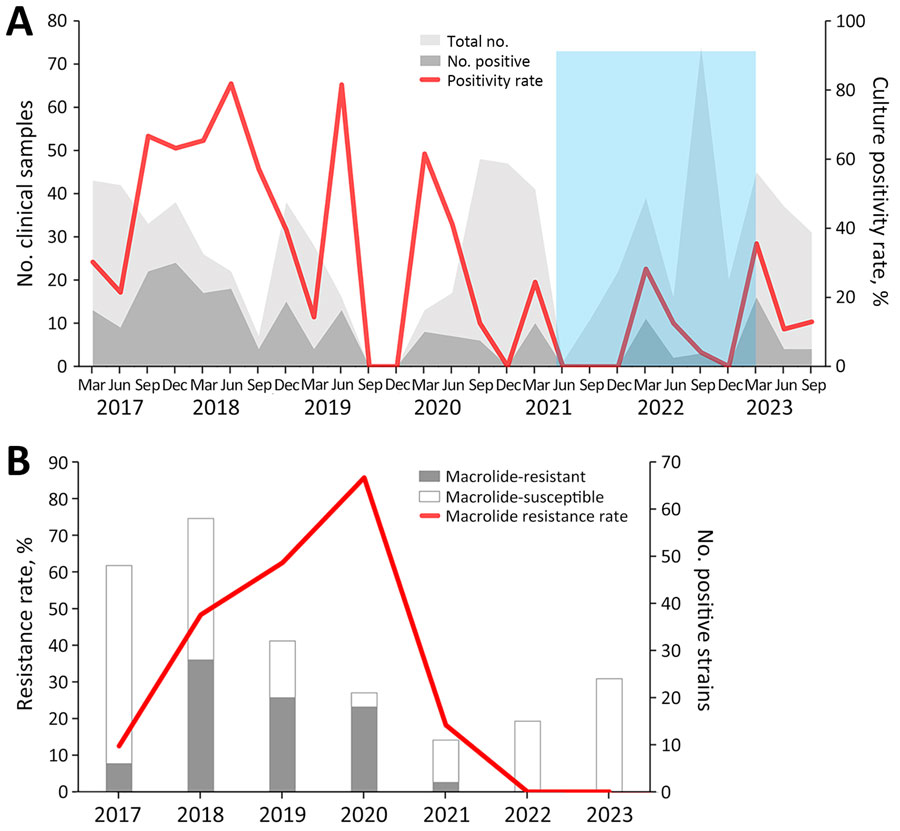
Figure 1. Dynamic distribution of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections among children before and during the COVID-19 pandemic, Taiwan, 2017–2023. A) M. pneumoniae infections were detected throughout the year, primarily from March to August. An M. pneumoniae outbreak occurred during 2017–2018. The M. pneumoniae detection rate substantially declined during the COVID-19 pandemic, 2021–2022. Light gray background represents 770 IgM-positive participants; dark gray background represents 209 cases confirmed by culture and PCR. Blue shading indicates timeframe of nonpharmaceutical interventions during the COVID-19 pandemic. B) Among 211 isolates, macrolide resistance was observed in 74 (35.1%) isolates. The resistance rate was 12.5% in 2017, increased to 48.3% in 2018 and to 62.5% in 2019, and reached 85.7% in 2020. Subsequently, the rate decreased to 18.2% in 2021 and dropped to 0% in 2022 and 2023.