Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Volume 31, Number 4—April 2025
Dispatch
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Stability in Irradiated Raw Milk and Wastewater and on Surfaces, United States
Figure 3
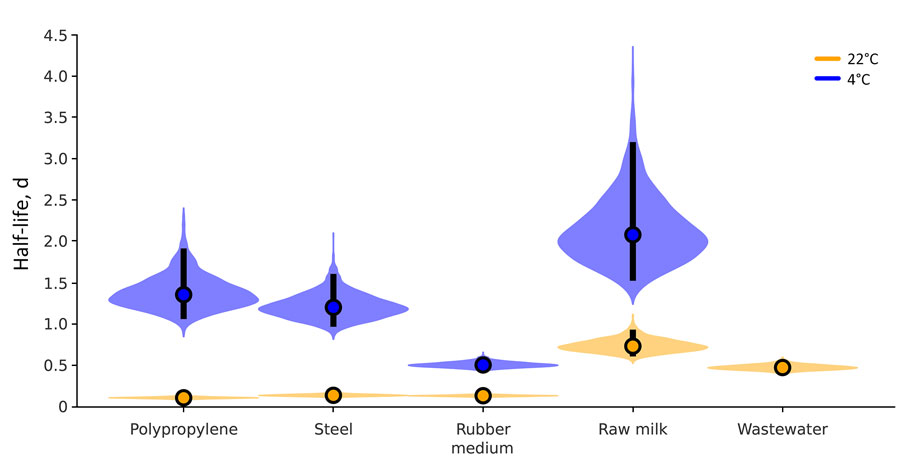
Figure 3. Violin plots showing results of experimental testing of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus stability in irradiated raw milk and wastewater and on surfaces, United States. Plots show the posterior distribution of the half-life of viable virus at each condition, determined from the estimated decay rates. Viral decay was calculated for H5N1 virus in irradiated raw milk at 22°C and 4°C, in irradiated wastewater at 22°C, and on polypropylene, steel, and rubber surfaces at 22°C and 4°C. The point at the center of each violin is the posterior median estimate, and the vertical black bars show 95% credible intervals (2.5%–97.5%).
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.