Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Volume 31, Number 5—May 2025
Research
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Outbreak in Endangered Cranes, Izumi Plain, Japan, 2022–23
Figure 3
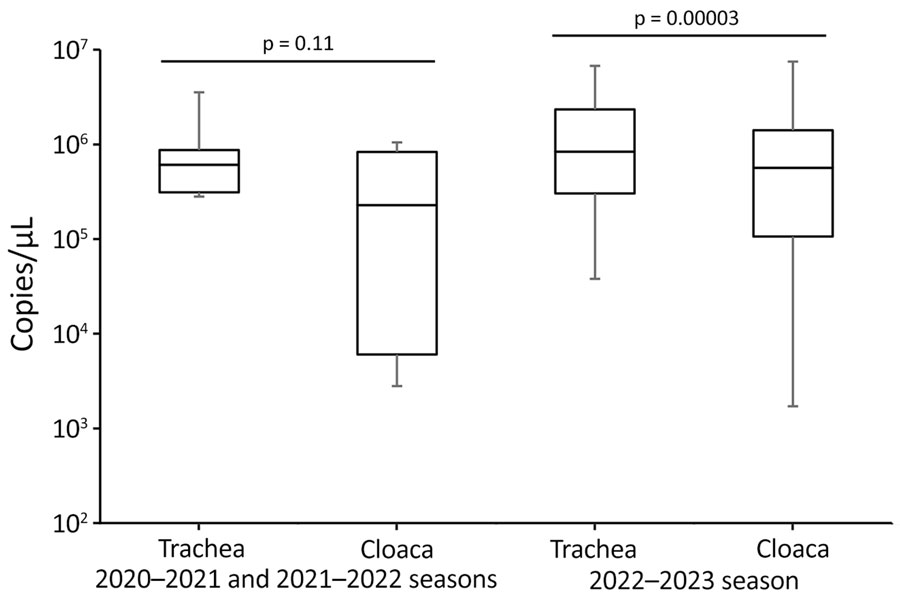
Figure 3. Box-and-whisker plot showing the distribution of copy numbers of the avian influenza virus (AIV) matrix (M) gene in swabs from AIV gene–positive cranes from the 2022–23 winter season compared with the combined 2020–21 and 2021–22 seasons in the Izumi Plain, Japan. We used RNA extracted from each AIV gene–positive swab sample for quantifying the copy number of the AIV M gene using real-time reverse transcription PCR. Boxes represent interquartile ranges; horizontal lines inside boxes indicates median; whiskers indicate maximum and minimum values. We evaluated significant differences between groups by paired t-test; p<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.