Volume 26, Number 11—November 2020
Research
Modeling Treatment Strategies to Inform Yaws Eradication
Figure 4
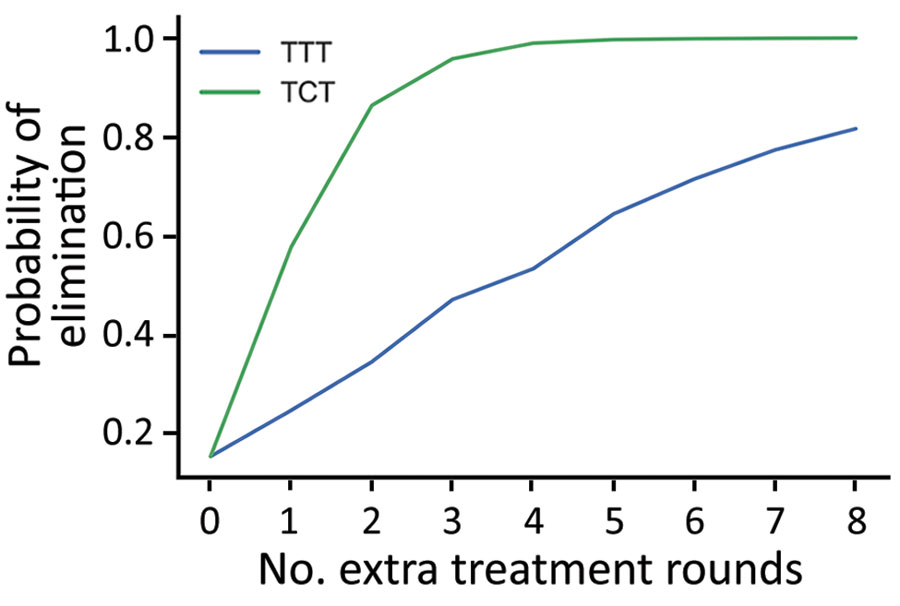
Figure 4. Probability of local elimination of transmission under different intervention strategies consisting of >2 rounds of TCT and >2 rounds of TTT, with varying numbers of additional rounds of TTT (blue) or TCT (green). Each twice-yearly round of TCT has 80% coverage, whereas TTT has 100% coverage and treatment is assumed to have 95% efficacy. All rounds of TCT are performed first before any rounds of TTT begin, which are then also performed twice yearly. Parameters are inferred from data collected from the Solomon Islands in 2013. TCT, total community treatment; TTT, total targeted treatment.
Page created: August 18, 2020
Page updated: October 17, 2020
Page reviewed: October 17, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.