Disclaimer: Early release articles are not considered as final versions. Any changes will be reflected in the online version in the month the article is officially released.
Volume 31, Number 4—April 2025
Research
Carbapenem-Resistant, Virulence Plasmid–Harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae, United States
Figure 4
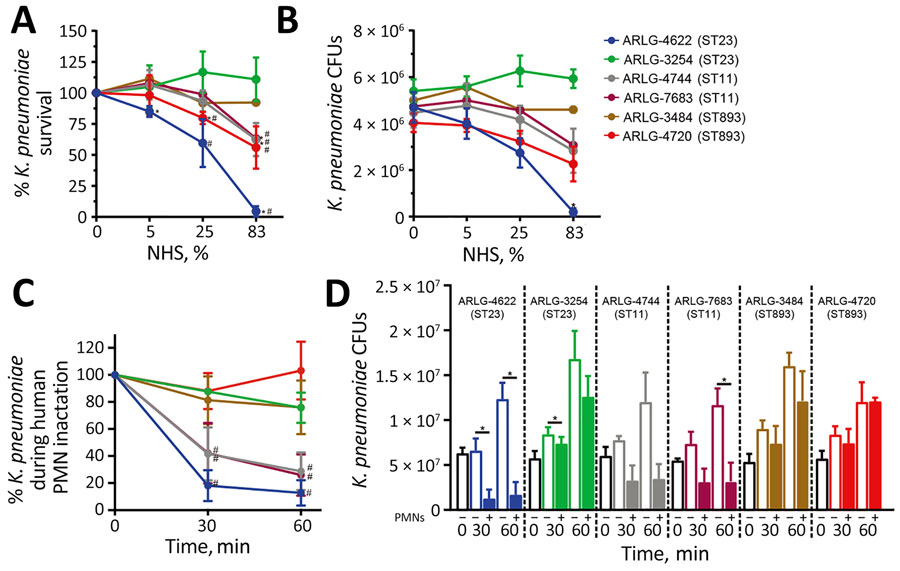
Figure 4. Serum and PMN bactericidal activity in 6 clinical isolates in study of carbapenem-resistant, virulence plasmid–harboring Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates, United States. A–B) The indicated clinical isolates were cultured with 0%, 5%, 25%, or 83% NHS for 1 hour, and recovered viable bacteria were enumerated as both percentages (A) and absolute values (B). Asterisk (*) indicates p<0.05 vs. 0% serum by using a repeated-measures analysis of variance and Dunnett posttest; hash mark (#) indicates p<0.05 vs. ARLG-3254 in 25% or 83% NHS by using a t-test. C–D) Survival of clinical isolates determined following synchronized PMN phagocytosis assays at 30 or 60 min as described. Data are expressed as percentage survival (C) or colony-forming units (D). Results represent the mean (dots) + SD (error bars) of 3 separate experiments. Asterisk (*) indicates p<0.05 as determined by using a repeated-measures analysis of variance and Bonferroni posttest (selected pairs of data) or Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn posttest for nonparametric analysis of ARLG-4744; hash mark (#) indicates p<0.05 vs. ARLG-3254 for 30 or 60 min in PMN by using a t-test. We conducted statistical analyses by using CFUs. NHS, normal human serum; PMN, polymorphonuclear neutrophils; ST, sequence type.